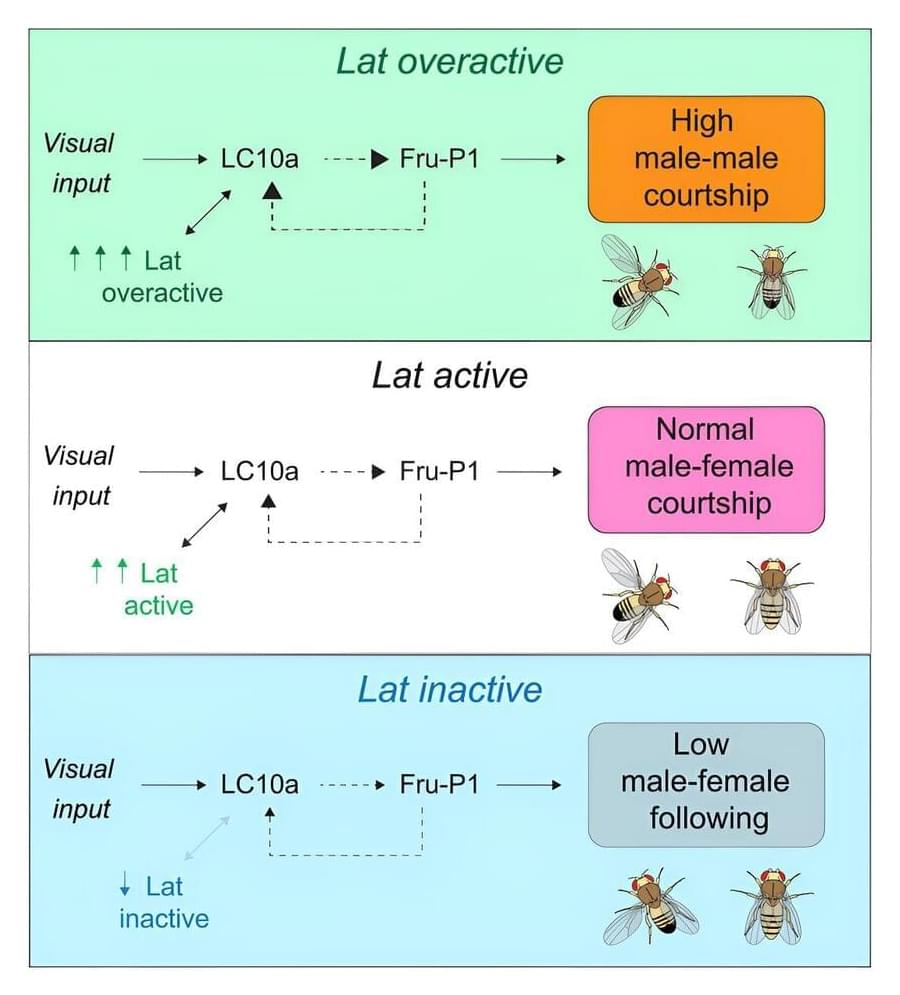
Male fruit flies don’t usually like each other. Socially, they reject their fellow males and zero in on the females they discern via chemical receptors—or so scientists thought.
New research from Cornell University biologists suggests the fruit fly’s visual system, not just chemical receptors, are deeply involved with their social behaviors. The work sheds light on the possible origin of differences in human social behaviors, such as those seen in people with bipolar disorder and autism.
The paper is published in Current Biology.