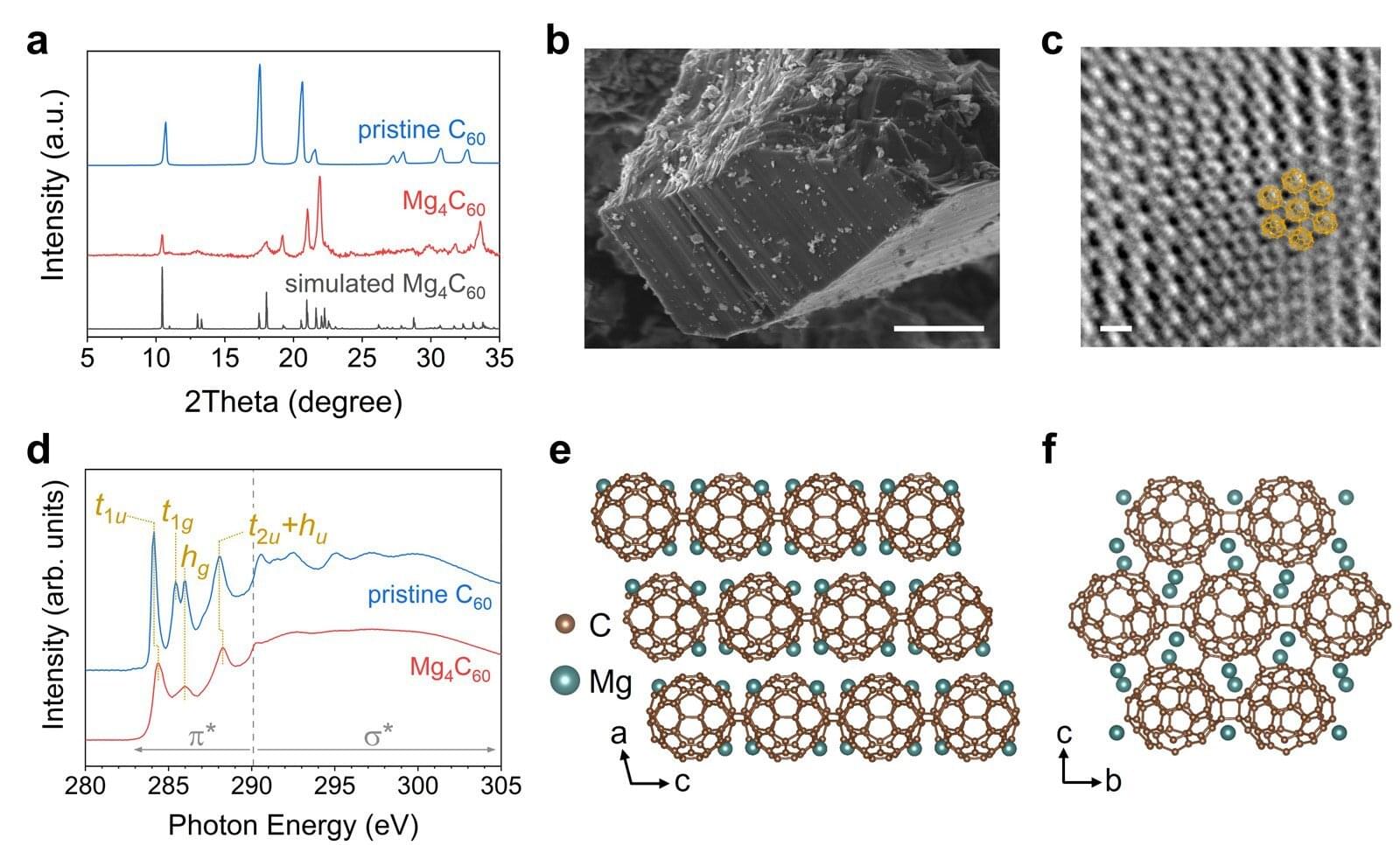
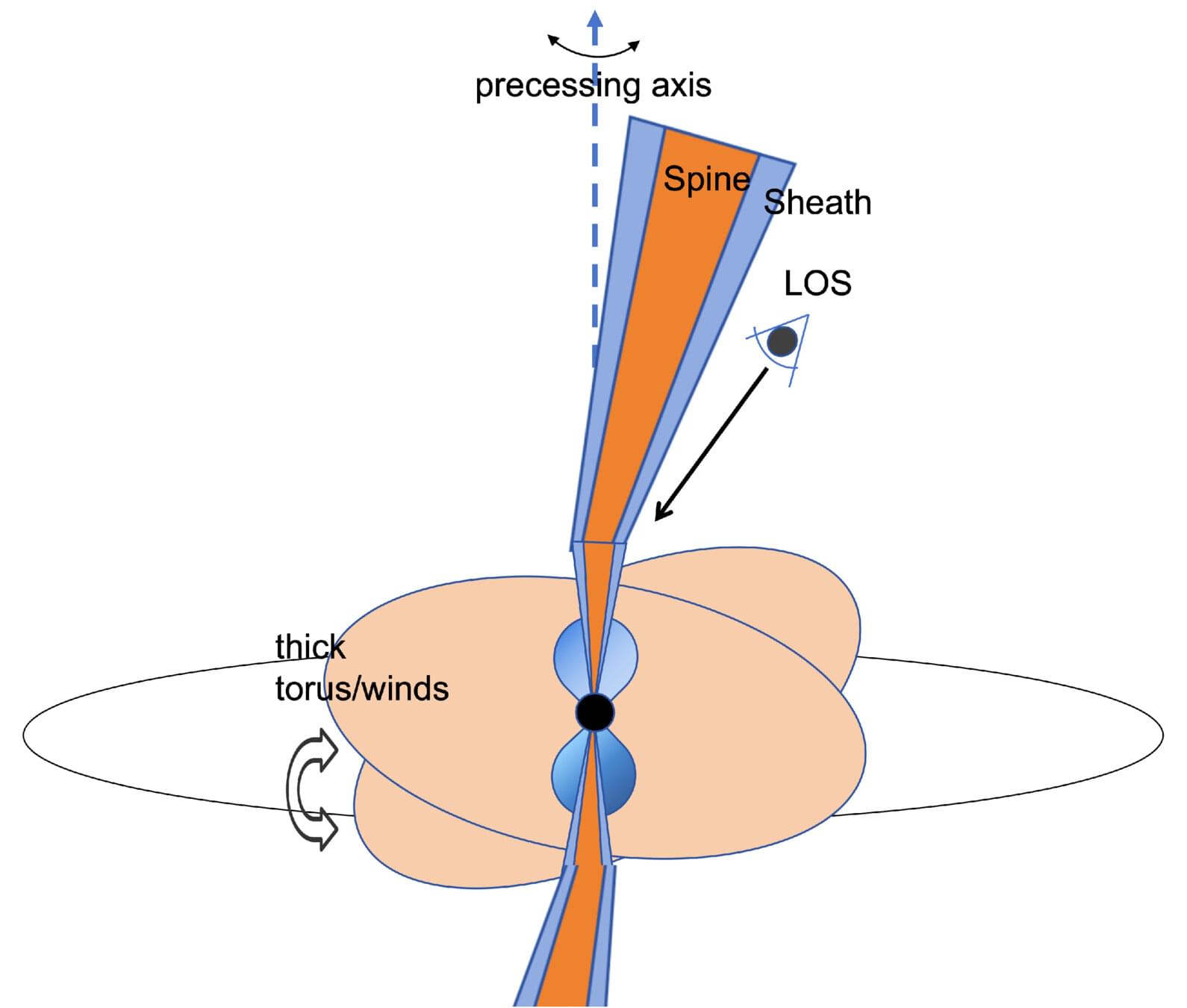
Prof. An Tao from the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory (SHAO) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a novel “precessing magnetic jet engine” model to explain the peculiar gamma-ray burst (GRB) 250702B, a rare cosmic explosion discovered on July 2, 2025.
This GRB exhibited periodic flares approximately every 47 minutes over more than three hours. The new model elucidates the physical origin of this “heartbeat” and resolves the mysteries surrounding its extremely hard spectrum and apparent excess energy. Results were published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on December 2.
GRB 250702B was detected by high-energy observatories, including the Fermi satellite and Konus-Wind. Its uniqueness lies in its temporal structure. The entire burst lasted approximately 3.2 hours and included three distinct, intense gamma-ray pulses with intervals that were integer multiples of a base period of about 2,825 seconds. Interestingly, approximately one day prior to this event, China’s “Einstein Probe” satellite detected a softer X-ray burst at the same location, acting as a precursor to the main event. This combination of “early warm-up plus hour-scale heartbeat” is extremely rare in GRB observations.