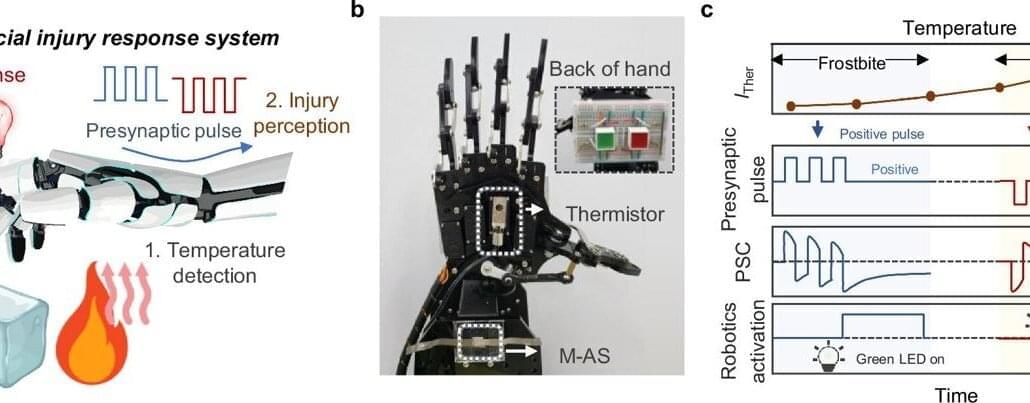
Engineers need good data to build lasting things. Even the designers of the Great Pyramids knew the limestone they used to build these massive structures would be steady when stacked on top of one another, even if they didn’t have tables of the compressive strength of those stones.
But when attempting to build structures on other worlds, such as the moon, engineers don’t yet know much about the local materials. Still, due to the costs of getting large amounts of materials off of Earth, they will need to learn to use those materials even for critical applications like a landing pad to support the landing / ascent of massive rockets used in re-supply operations.
A new paper published in Acta Astronautica from Shirley Dyke and her team at Purdue University describes how to build a lunar landing pad with just a minimal amount of prior knowledge of the material properties of the regolith used to build it.