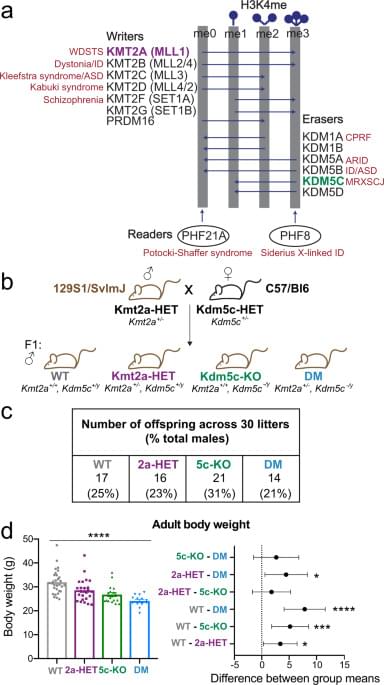
Vallianatos et al. study the functional interactions of KMT2A and KDM5C, H3K4me enzymes known to be involved in neurodevelopmental disorders. Using genetic mouse models, neuronal structure analysis, neurobehavior, and epigenomic profiling, they demonstrate a mutually suppressive relationship between KMT2A and KDM5C during neurodevelopment.