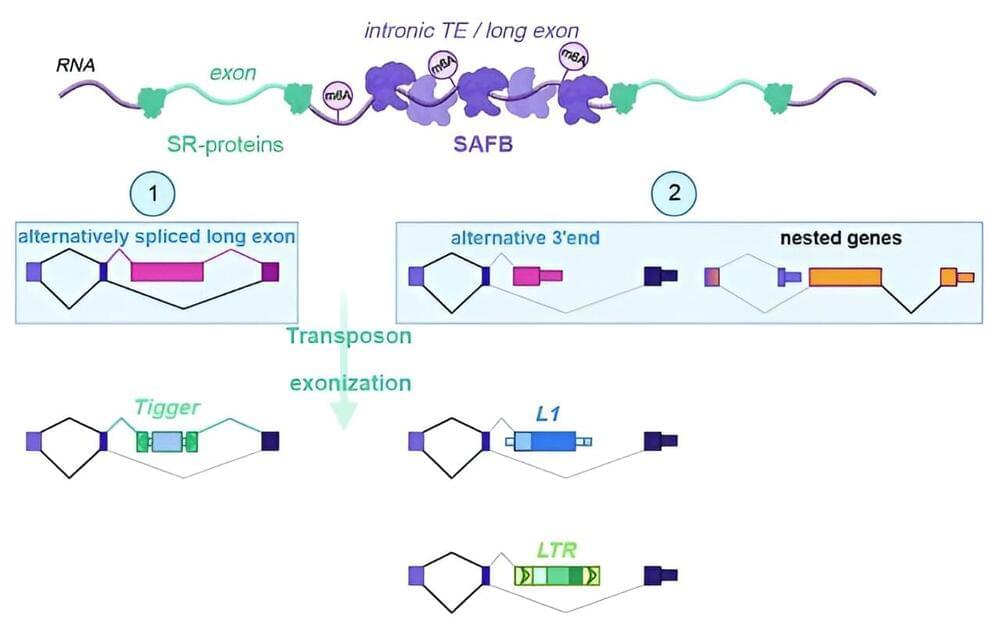
Transposable elements are mobile genetic elements that can relocate within the genome and disrupt the normal function of genes, but are at the same time a source of evolutionary diversity. The lab of Tugce Aktas at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics has identified a novel pathway that keeps the activity of transposons in somatic cells in check after they have been transcribed.
Their findings have now been published in Nature. The work is a collaboration with the labs of Zachary D. Smith at the Yale Stem Cell Center, U.S., and Franz-Josef Müller from the Universitätsklinikum Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.
Over the course of evolution, the genomes of many organisms have become cluttered with ancient genetic remnants from evolution or parts of retroviruses that inserted their genetic code millions of years ago. Nearly half of the human genome consists of these transposable elements, or transposons.