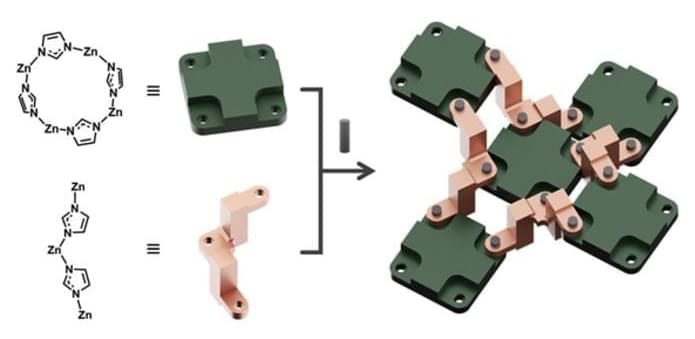
Machines have evolved to meet the demands of daily life and industrial use, with molecular-scale devices often exhibiting improved functionalities and mechanical movements. However, mastering the control of mechanics within solid-state molecular structures remains a significant challenge.
Researchers at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), South Korea have made a groundbreaking discovery that could pave the way for revolutionary advancements in data storage and beyond. Led by Professor Wonyoung Choe in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST), a team of scientists has developed zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) that mimic intricate machines. These molecular-scale devices can exhibit precise control over nanoscale mechanical movements, opening up exciting new possibilities in nanotechnology.
The findings have been published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition (“Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks as Solid-State Nanomachines”).