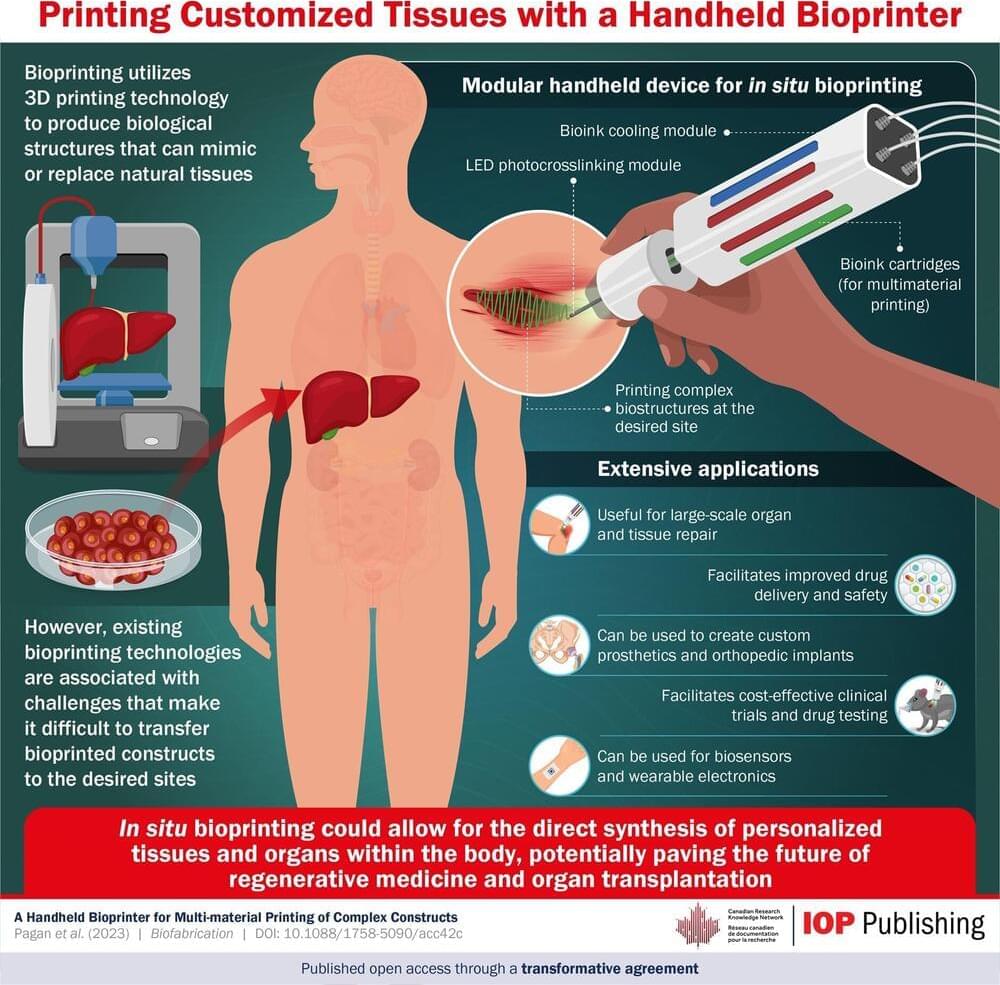
Cultured meat starts with the extraction of cells from an animal’s tissue, be it a pig, cow, chicken, fish, or any other animal we consume. The cell extraction doesn’t kill or even harm the animal. The cells are mixed with a cocktail of nutrients, oxygen, and moisture inside large bioreactors. Mimicking the environment inside an animal’s body, the bioreactors are kept at a warm temperature, and the cells inside divide, multiply, and mature. Waste products are regularly removed to keep the environment pure.
Once the cells have reached maturity—that is, grown into small chunks of muscle-like material—they’re harvested from the bioreactors to be refined and shaped into a final product. This can involve anything from extrusion cooking and molding to 3D printing and adding in artificial fat.
JBS says the factory it’s building in Spain will be able to produce more than 1,000 metric tons of cultivated beef per year, and could expand capacity to 4,000 metric tons per year in the medium term. That’s smaller than Believer Meats’ facility in the US, which will have an annual production capacity of 10,000 metric tons. But what’s noteworthy about the JBS factory is that it’s focused on producing beef.