Though it may be hard to believe that there is already an “established” method of doing something such as 3D-printing biological tissue, there does indeed seem to be one. It utilizes microscale scaffolds – which a newly-developed technique does away with the need for.
Category: 3D printing – Page 77
Adam Savage Made Real Life Flying Iron Man Armor
Adam Savage has made bullet-proof Iron Man Armor using 3D printed titanium and a flying jet suit from Gravity.
It is more precisely a real-life Titanium Man (comic book enemy of Iron Man).
The US military (Special Ops) recently canceled an attempt to make real-life iron man exoskeleton armor with strength enhancement. They are looking to use components of the system to help boost the strength of joints and to increase light-weight armor protection for many soldiers.

Technology Platform
Kyle Reese: The Terminator’s an infiltration unit, part man, part machine. Underneath, it’s a hyperalloy combat chassis — micro processor-controlled, fully armored. Very tough. But outside, it’s living human tissue — flesh, skin, hair, blood, grown for the cyborgs…
3D bioprinting is the automated fabrication of multicellular tissue via spatially defined deposition of cells. The ability to spatially control deposition in the x, y and z axes allows for creation of tissue-specific patterns or compartments, with in vivo-like architecture that mimics key aspects of native biology.
3D bioprinted tissues exhibit a microenvironment more suited to in vivo-like cellular function in comparison to traditional 2D monoculture (or monolayer co-cultures), as well as maintenance of a more defined architecture than is observed in self-aggregated co-culture models.


Can Self-Replicating Robots Lead To A Society Without Scarcity?
The status quo of economies today seems to be leaning towards automation as the base provider of all products and services. Owing to rise of robots in factories and AI in computing, automation is becoming one of the most integral parts of society.
While self-replicating robots have largely been kept to science fiction books, their rise is becoming more and more likely with the rise of supplementary technologies such as 3D printing.
This technology could hold the key to a truly post-scarcity society. The question then arises, how would the rise of a post-scarcity society affect human institutions such as economy and governance that rely on scarcity?
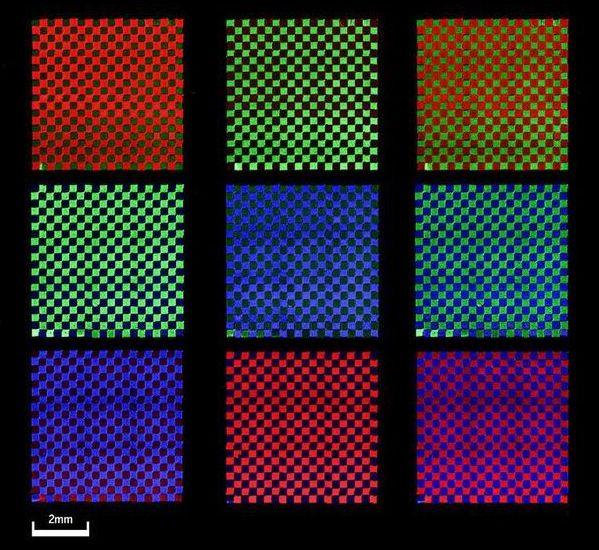
LEDs created from wonder material could revolutionize lighting and displays
In solar cells, the cheap, easy to make materials called perovskites are adept at turning photons into electricity. Now, perovskites are turning the tables, converting electrons into light with an efficiency on par with that of the commercial organic light-emitting diodes (LEDs) found in cellphones and flat screen TVs. And in a glimpse of how they might one day be harnessed, researchers reported last week in Science Advances that they’ve used a 3D printer to pattern perovskites for use in full-color displays.
“It’s a fantastic result, and quite inspirational,” says Richard Friend, a physicist at the University of Cambridge in the United Kingdom whose team created the first perovskite LED in 2014. The result raises hopes that the computer screens and giant displays of the future will consist of these cheap crystalline substances, made from common ingredients. Friend cautions, however, that the new perovskite displays aren’t yet commercially viable.
The materials in current semiconductor LEDs, including the organic versions, require processing at high temperatures in vacuum chambers to ensure the resulting semiconductors are pristine. By contrast, perovskites can be prepared simply by mixing their chemical components in solution at room temperature. Only a brief heat treatment is needed to crystallize them. And even though the perovskite crystals end up with imperfections, these defects typically don’t destroy the materials’ ability to emit light.