Harvard University geneticist George Church says reaction to experiments has been “extreme”.


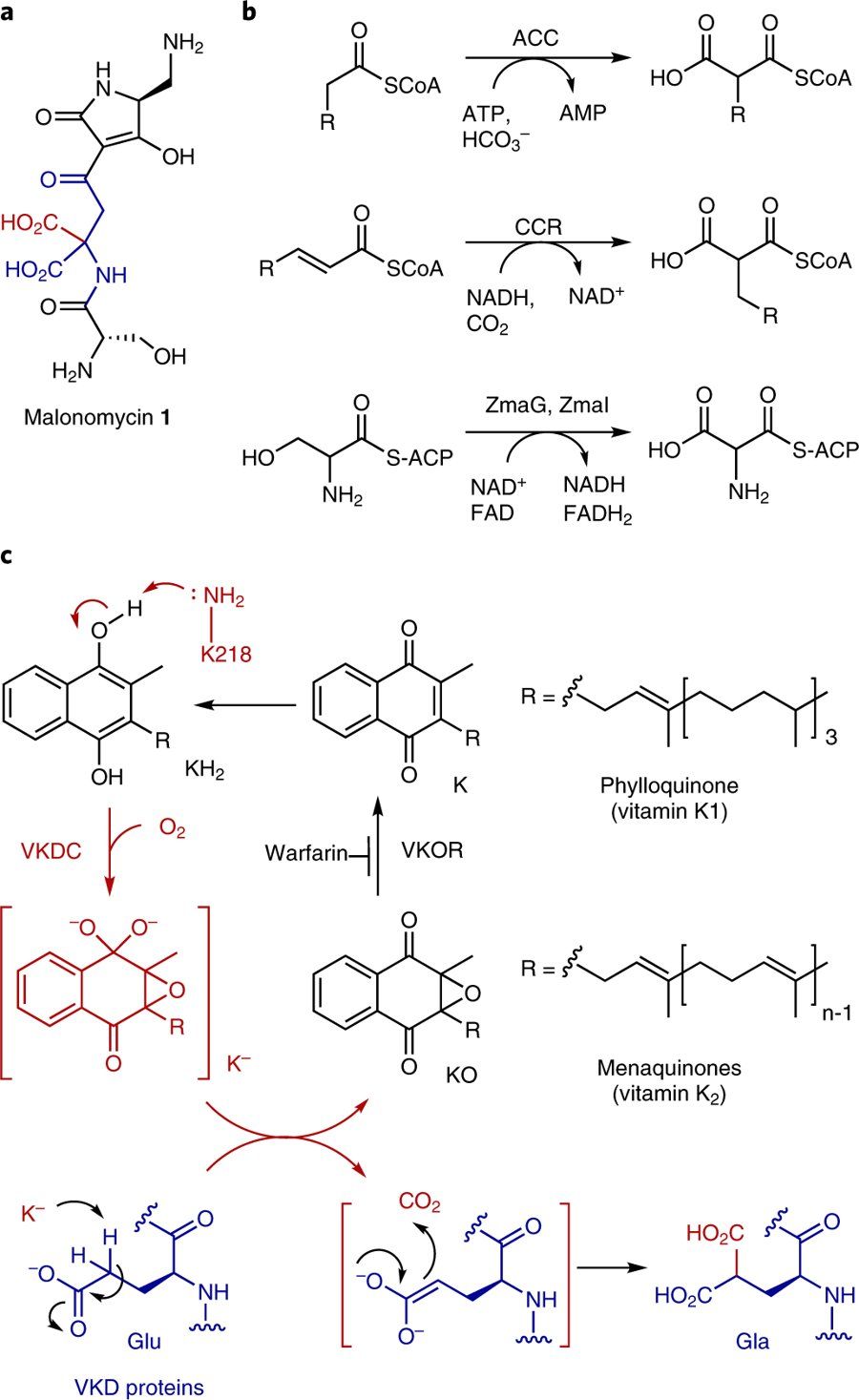
Scientists have discovered a new chemical process—also known as a biosynthetic pathway—in bacteria which could lead to a new generation of antibiotics being produced and manufactured.
Researchers at The University of Manchester’s School of Chemistry say their new pathway includes an enzyme, called a carboxylase, which adds CO2 to a precursor molecule producing a highly unusual antibiotic called malonomycin.
The team says the biosynthetic process used to produce this antibiotic could now possibly lead to the discovery and development of other drugs, helping in the fight against drug-resistant bugs and illnesses in the future.

Not sure if this is real or still vaporware yet. But it IS inevitable. It’s not a matter of “if”, but “when”. And we’re most likely not going to be able to regulate it much, either. If an embryo or fetus is not a human, then parents have the right to do anything they want to it. You might think that this is going to result in eugenics, like erasing melanin genes and starting a race against the fictitious “white genocide”. You’re right. But if you think that’s as bad as it’ll get, think more creatively. What happens when poor parents get paid to implant “willing servility” genes into their unborn children, in order to pay bills. The future is now. Cyborgs will not destroy humanity, but humanity itself might. What kinds of rights can be written into law to prevent this kind of extortion, that won’t also grant fetal personhood and end up derailing abortion rights? It’s going to be a bumpy ride, folks, buckle up!
A Chinese researcher claims he helped make the world’s first genetically edited babies — twin girls born this month, and with DNA he says he altered with a powerful new tool capable of rewriting the very blueprint of life.
If true, it would be a profound leap of science and ethics.
A U.S. scientist said he took part in the work in China, but this kind of gene editing is banned in the United States because the DNA changes can pass to future generations and risks harming other genes.
And so it begins…
HONG KONG (AP) — A Chinese researcher claims that he helped make the world’s first genetically edited babies — twin girls born this month whose DNA he said he altered with a powerful new tool capable of rewriting the very blueprint of life. If true, it would be a profound leap of science and ethics. A U.S. scientist said he took part in the work in China, but this kind of gene editing is banned in the United States because the DNA changes can pass to future generations and it risks harming other genes. Many mainstream scientists think it’s too unsafe to try, and some denounced the Chinese report as human experimentation.


WASHINGTON (AP) — The next generation of biotech food is headed for the grocery aisles, and first up may be salad dressings or granola bars made with soybean oil genetically tweaked to be good for your heart.
By early next year, the first foods from plants or animals that had their DNA “edited” are expected to begin selling. It’s a different technology than today’s controversial “genetically modified” foods, more like faster breeding that promises to boost nutrition, spur crop growth, and make farm animals hardier and fruits and vegetables last longer.
The U.S. National Academy of Sciences has declared gene editing one of the breakthroughs needed to improve food production so the world can feed billions more people amid a changing climate. Yet governments are wrestling with how to regulate this powerful new tool. And after years of confusion and rancor, will shoppers accept gene-edited foods or view them as GMOs in disguise?