Two heads are better than one, as the saying goes, and sometimes two instruments, ingeniously recombined, can accomplish feats that neither could have done on its own.
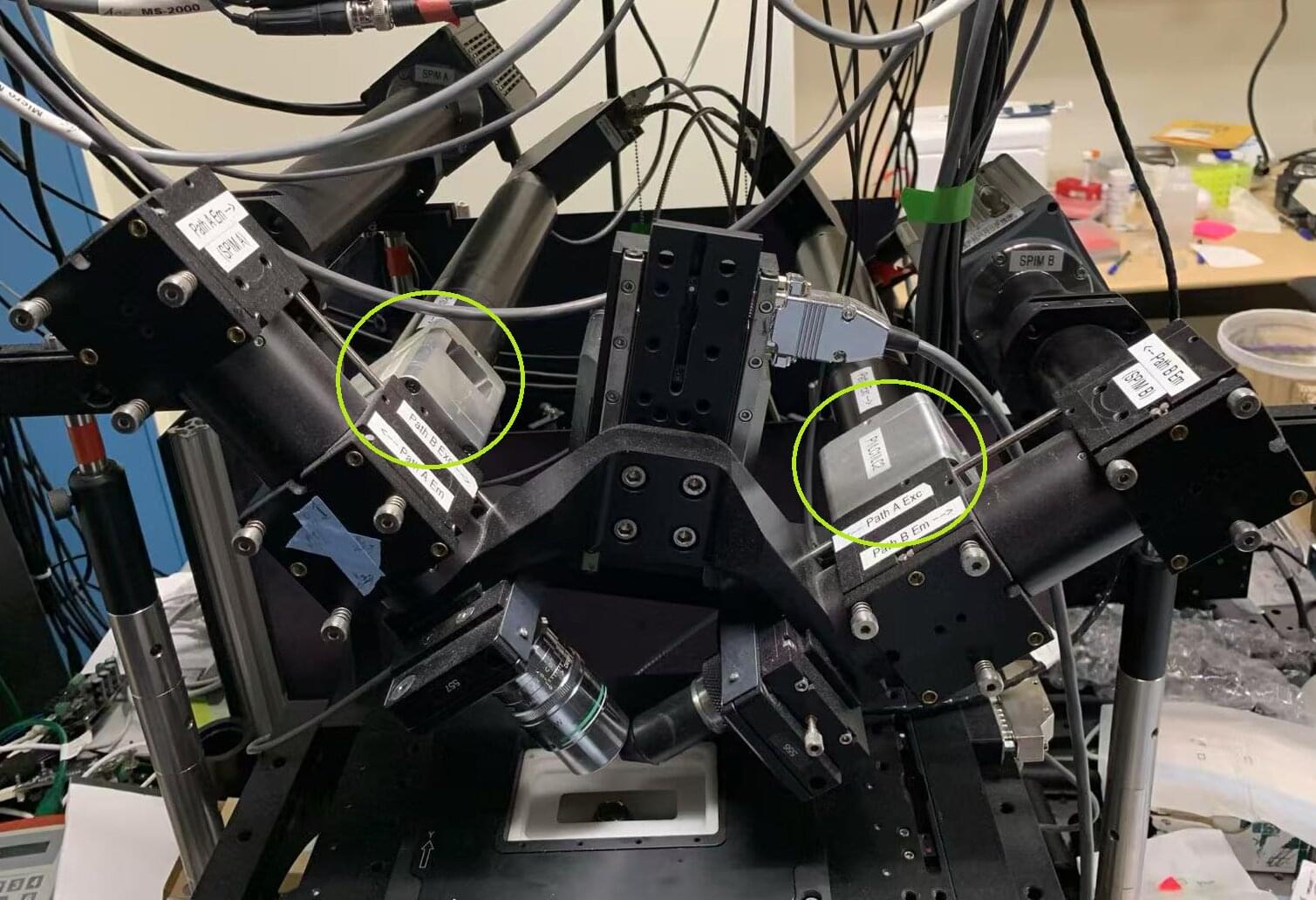
Such is the case with a hybrid microscope, born at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), that for the first time allows scientists to simultaneously image the full 3D orientation and position of an ensemble of molecules, such as labeled proteins inside cells. The research is published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The microscope combines polarized fluorescence technology, a valuable tool for measuring the orientation of molecules, with a dual-view light sheet microscope (diSPIM), which excels at imaging along the depth (axial) axis of a sample.