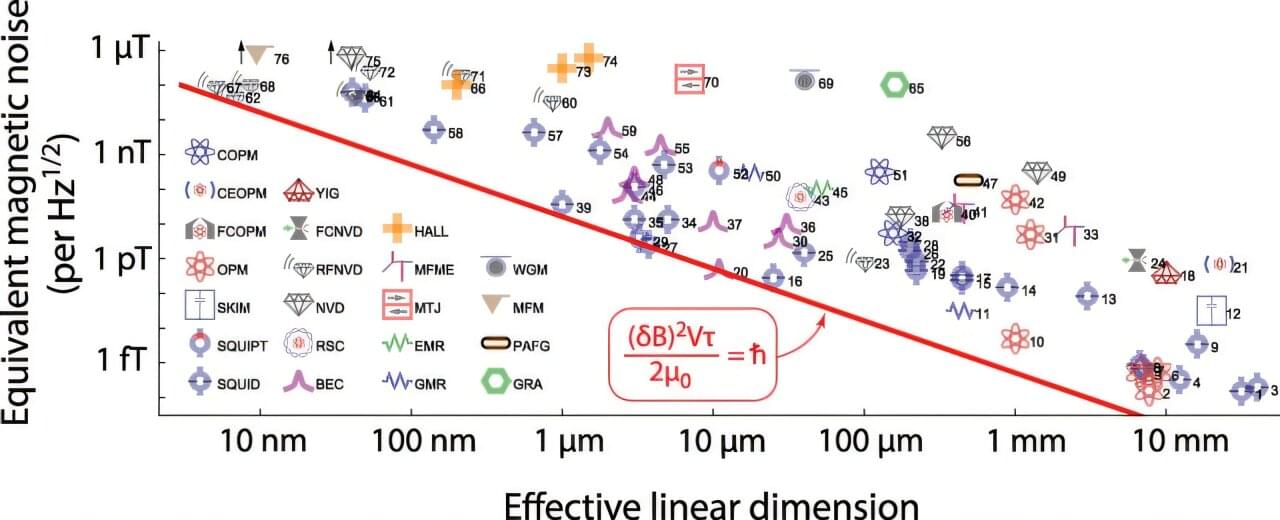
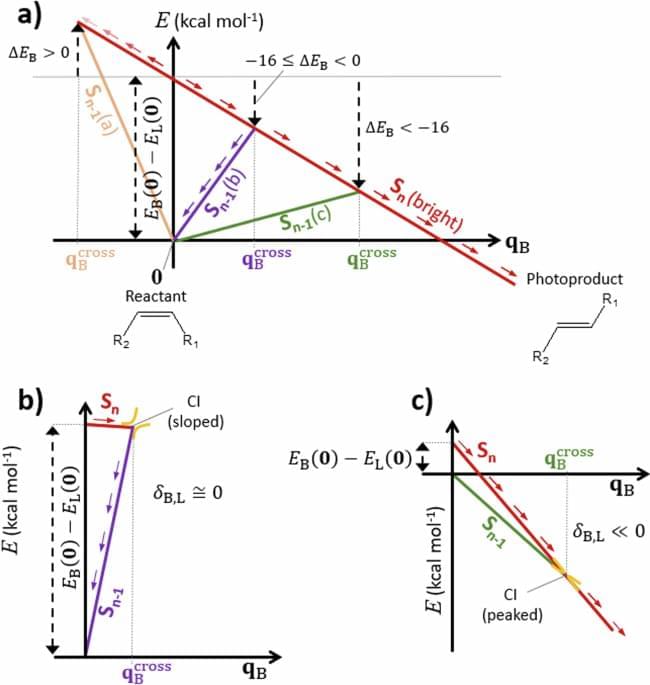
A pair of physicists at the University of Crete has found that some types of biological magnetoreceptors used by various creatures to navigate, operate at or near the quantum limit. In their paper published in the journal PRX Life, I. K. Kominis and E. Gkoudinakis describe how they worked the problem of magnetic sensing in tiny animals in reverse by putting bounds on unknown quantum boundaries, and what it showed about the navigation abilities of certain animals.
Prior research has shown that many creatures use the Earth’s magnetic field as a navigation aid. Some sharks, fish and birds, for example, use it to help them traverse long distances. Different animals also have different types of magnetic sensors, including radical-pair, induction and magnetite mechanisms.
Radical-pair works by sensing correlations between unpaired electrons attached to certain molecules. Induction works by turning energy in the magnetic field into electricity and then sensing the electrical charge. And magnetite-based magnetoreception involves sensing the movement or orientation of tiny iron crystals in the body, similar to a human-made compass.