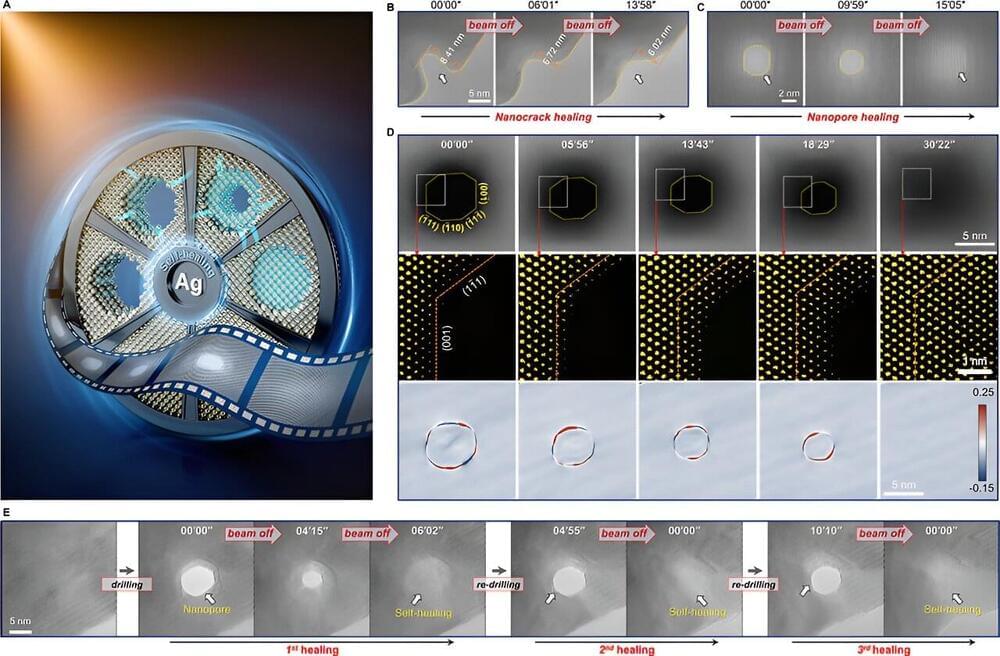
In science fiction movies like Frankenstein and Re-Animator, human bodies are revived, existing in a strange state between life and death. While this may seem like pure fantasy, a recent study suggests that a “third state” of existence might actually be present in modern biology.
According to the researchers, this third state occurs when the cells of a dead organism continue to function after its death, sometimes gaining new capabilities they never had while the organism was alive.
Amazingly, if further experiments on cells from dead animals — including humans — prove this ability, it could even challenge the definition of legal death.