Research in immunotherapy identifies mechanism that helps fight lung cancer and melanoma.
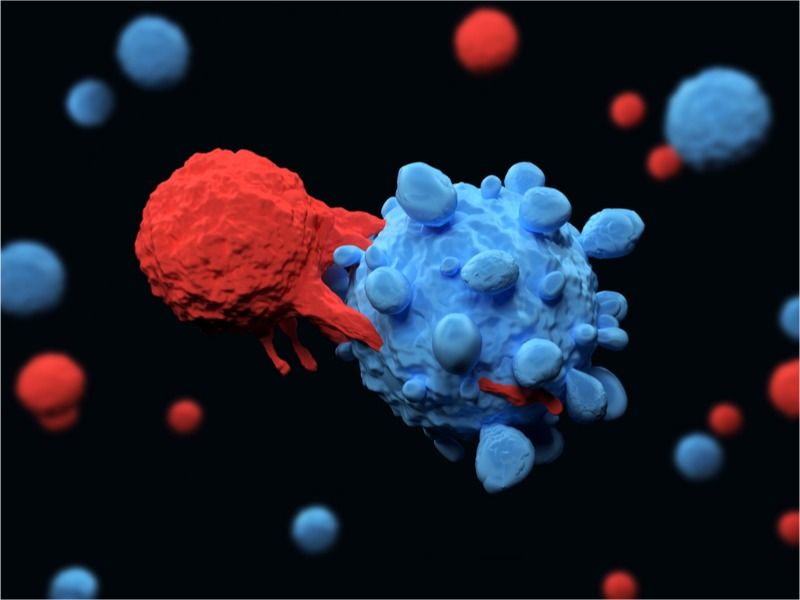
In a breakthrough discovery, scientists from Harvard Medical School along with a team at Bar-Ilan University have uncovered a mechanism in which the immune system is capable of attacking cancer cells. This contributes greatly to research in immunotherapy, particularly in fighting lung cancer and melanoma (skin cancer). The research team was composed of Prof. Nick Hainin of Harvard Medical School and Prof. Erez Levanon of the Mina and Everard Goodman Faculty of Life Sciences at Bar-Ilan University, along with doctoral student, Ilana Buchumansky and many others.
The study was published two weeks ago in the journal Nature, detailing how scientists have uncovered a mechanism that assists the cell by leaving markers on human virus-like genes thereby preventing them from being recognized as viruses. When this channel is inhibited, the immune system can be utilized to destroy cancerous cells, particularly in the cases of lung cancer and melanoma. The immune system reacts when this path is blocked or shut off, and allows the body to destroy cancer cells at a more effective rate.