We looked into whether these for-profit clinics will really help you.




Merry Christmas
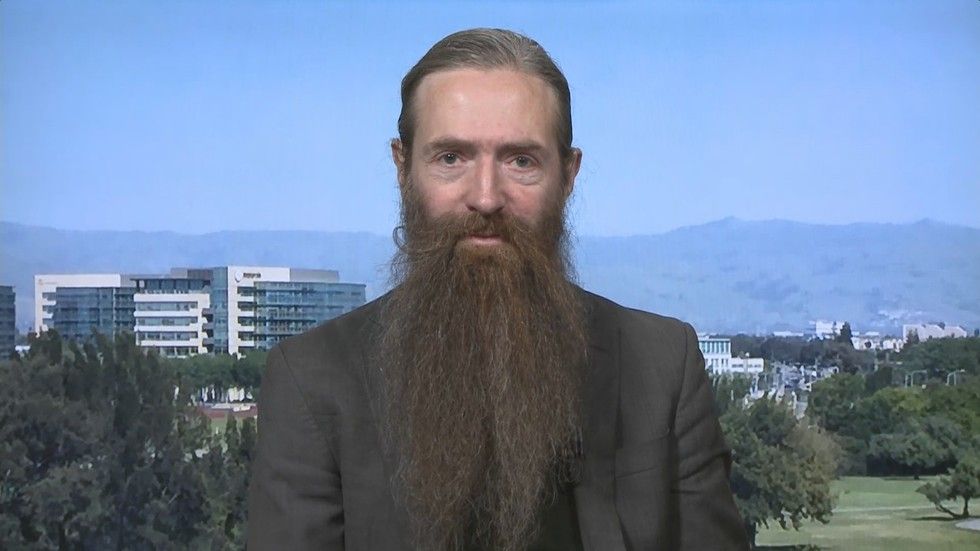
Is the Fountain of Youth still just a dream, or does hope spring eternal when it comes to beating the curse of aging? Having haunted us for centuries, is a solution finally within our grasp? We spoke to Dr Aubrey de Grey, anti-aging pioneer, chief science officer, and co-founder of SENS Research Foundation.
Follow @SophieCo_RT
Sophie Shevardnadze: Dr. Aubrey de Grey, anti-aging pioneer, chief science officer and co-founder of SENS Research Foundation, welcome to the show, great to have you with us. So what you propose in order to reverse aging is cleaning the organism of all the junk that accumulates there on the cellular level. Tell me the gist of it – why will that stop the wearing of time on my organs?
Aubrey de Grey: Well, it’s not quite that simple. What we propose is that we can keep people healthy late in life by repairing all of the damage that the body does to itself throughout life in the cause of its normal operation. And some of that damage is of the sort that you’ve just described, essentially, the accumulation of waste products both inside cells and also in the spaces between cells. But some of this is not quite like that. For example, sometimes simply we have too many of a particular bad type of cell that is misbehaving, or, in other cases, we don’t have enough cells of a particular good type. Cells die, and they are not necessarily replaced automatically by the division of other cells. Furthermore, there is damage to the structure, the kind of lattice of proteins that holds the body together, which is called the extra-cellular matrix. So, as you can see, there are many different types of damage, and we have to fix them all.

Companies use different algorithms based on different sets of data. Most of that data comes from people of recent European ancestry.
The problem, obviously, is that a lot of people don’t have grandparents or great-great-great-grandparents from England or Italy or Denmark. Most people on Earth, actually! That means if you’re from, say, Asia or Africa, you might not get as detailed a profile as you’d like.
My mother, who was born in the Philippines, actually got an update from 23andMe with new information about her heritage. Her history didn’t change. But as the company gets more DNA kits from people of Asian descent, the algorithm churns out modified results. Which is great … but that does mean right now, if you’re not white, you might have to wait a bit longer for more accurate results.

New program coming on-line at Bioquark Inc. (www.bioquark.com) — Ectocrine interactions (the“Ectocrinome”) represents a completely unexplored area related to human health
https://www.prweb.com/releases/bioquark_inc_and_ectocrine_te…004155.htm
Building on several years of research into a protein responsible for leukemia, a newly published paper has revealed success in slowing the progression of the deadly cancer in mouse models. The researchers suggest two new prospective therapies can now be combined into one “super drug” and progress into human clinical trials.