Desiccants kill more than plants. Herbicides like glyphosate also kill bacteria. You could just as easily call them “antibiotics.” Our gut bacteria are sensitive to antibiotics, which is why we should avoid eating herbicides. When our microbes are healthy, our immune system is stable. But when microbes are disturbed, diseases like obesity, Alzheimer’s, or celiac disease can result.
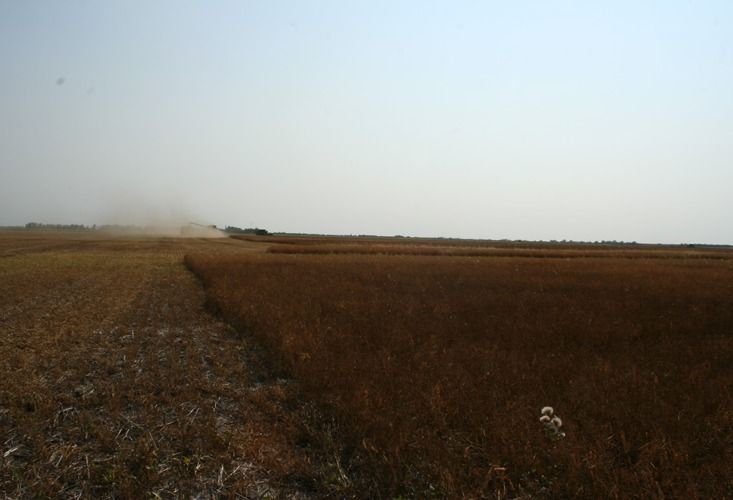
Driving down a grid road in central Saskatchewan, a machine that looks like a giant insect approaches me in a cloud of dust. The cab, hanging 8 feet above the road, is suspended by tires at least 6 feet tall, with wing-like appendages folded along each side. Should I drive around it or under it?
It is harvest season, and the high-clearance sprayer is on its way to desiccate a field. Desiccation may be the most widespread farming practice you’ve never heard of. Farmers desiccate by applying herbicide to their crops; this kills all the plants at the same time, making them uniformly dry and easier to cut. In essence, desiccation speeds up plant aging. Before desiccation, crops would have to dry out naturally at the end of the season. Today, almost all conventional crops are desiccated in Canada, the United States, and the United Kingdom. Chances are that most of what you ate today was harvested using a desiccant, but you’d never know.
Mike Shewchuk jumps down from his swather as I pull into his farmyard. He is a young farmer whose blond brush cut and a robust stride would have not been out of place 50 years ago. Along with his dad, uncles, and brother, he farms 15,000 acres an hour outside of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. They recently received a century farm award, for having continuously farmed the land since the early 1900s.