Sounds neat.
Memories are transferred from one snail to another in a laboratory.

New video from Undoing Aging 2018: Mike West, Founder, and CEO of AgeX, presenting their work on induced tissue regeneration: Leveraging the unique regenerative potential of pluripotent stem-cell-derived therapeutics.
Accelerating rejuvenation therapies to repair the damage of aging. Berlin, March, 15 — 17.
New video from Undoing Aging 2018: John Lewis, CTO of Oisín Biotechnologies presenting their work developing very selective therapies to kill senescence cells.
Accelerating rejuvenation therapies to repair the damage of aging. Berlin, March, 15 — 17.
Research on people’s reaction to life extension is rather rare; this article discusses two such papers.
Two papers by Partridge et al [1, 2], both published in 2009, provide the somewhat rare opportunity to examine some concerns about life extension as formulated by actual people, rather than their general, more abstract forms. As highlighted in the studies, research on the public’s perception of life extension science has been very much neglected; this, in turn, has made it harder to identify the misconceptions and incorrect information fueling some common concerns about life extension and made it even harder to address those very concerns. Needless to say, the more that the public views life extension negatively, the less supportive that it will probably be, which is bad news for researchers.
The papers present the results of several interviews, conducted either in person or on the phone, aimed at understanding what ethical concerns the interviewees had about life extension and what implications they thought extended human lifespans would have for themselves and for society. The research was conducted on a sample of the Australian population only, but the issues they raised were entirely representative of a typical discussion about life extension. In both studies, the interviewees were presented with the general premise of possibly slowing down aging and the onset of age-related diseases in order to greatly extend human healthy lifespan.
We’ll be taking a look at specific claims made or sentiments expressed by different interviewees in both studies.

Who wants to lose weight, feel great, and live a long and healthy life, and what does it take to achieve these goals? Diet and exercise are equally important in long-term health, but let’s look at what recent science is telling us about the healthiest diets.
This article will rely heavily on University of Southern California professor Valter Longo’s work because I consider it to be the gold standard for nutrition research, and his recommendations in his book The Longevity Diet are well-supported with both data and good logic. Longo is the director of the Longevity Institute at USC and the IFOM Program on Longevity and Cancer in Milan.
He comes from an area of Italy known for very long lives, and part of his research focus has been looking at similar areas around the world and why those people live so much longer than normal.
Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have discovered that as we age, our cells’ nuclear membranes become misshapen, which stops our genes from working properly.
Nuclear membranes become distorted with age
The DNA in all our cells is the same; however, the cells in our body show a great range of variation and function. How can this be when they have the same DNA? It all comes down to gene expression and which genes are turned off and which are turned on. For example, certain genes must be turned on in a cell for it to be a liver cell; those same genes need to be turned off for it to be a brain cell. If the correct genes are not turned off, problems occur.
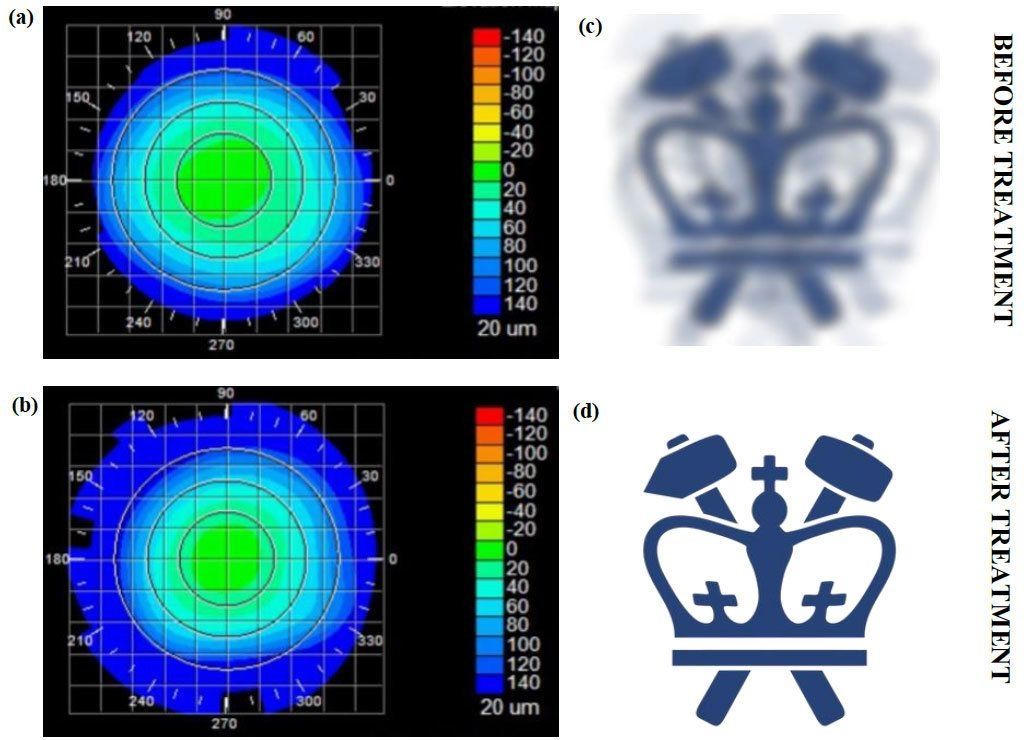
Nearsightedness, or myopia, is an increasing problem around the world. There are now twice as many people in the US and Europe with this condition as there were 50 years ago. In East Asia, 70 to 90 percent of teenagers and young adults are nearsighted. By some estimates, about 2.5 billion of people across the globe may be affected by myopia by 2020.
Eye glasses and contact lenses are simple solutions; a more permanent one is corneal refractive surgery. But, while vision correction surgery has a relatively high success rate, it is an invasive procedure, subject to post-surgical complications, and in rare cases permanent vision loss. In addition, laser-assisted vision correction surgeries such as laser in situ keratomileusis (LASIK) and photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) still use ablative technology, which can thin and in some cases weaken the cornea.
Columbia Engineering researcher Sinisa Vukelic has developed a new non-invasive approach to permanently correct vision that shows great promise in preclinical models. His method uses a femtosecond oscillator, an ultrafast laser that delivers pulses of very low energy at high repetition rate, for selective and localized alteration of the biochemical and biomechanical properties of corneal tissue. The technique, which changes the tissue’s macroscopic geometry, is non-surgical and has fewer side effects and limitations than those seen in refractive surgeries. For instance, patients with thin corneas, dry eyes, and other abnormalities cannot undergo refractive surgery. The study, which could lead to treatment for myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and irregular astigmatism, was published May 14 in Nature Photonics.