1. A heart of foam.
2. Artificial arteries.
3. Brain implants.
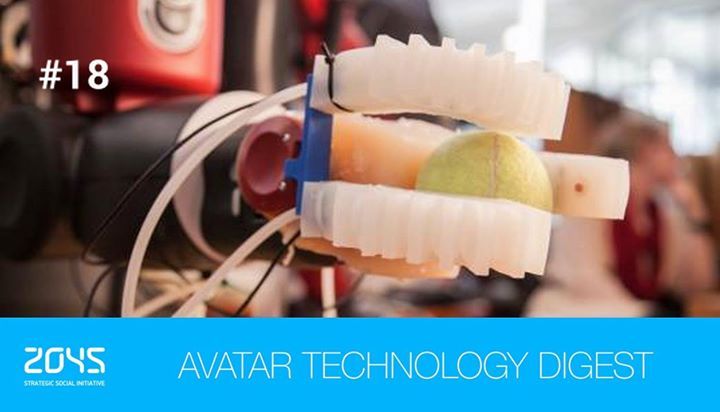
4. Robotic hand that can recognize objects by Feel.
5. Upside-Down Rover to explore Europa.
Welcome to #18 Avatar Technology Digest. Again, get ready for exciting news on Technology, Medical Cybernetics and Artificial Intelligence. Thank you for watching us. You are welcome to Subscribe, follow us in social media, leave your comments and join the conversation. And here are the top stories of the last week.
1) A heart of foam could replace your own. Existing artificial hearts have multiple moving parts, which increases the chance of failure, but this new device is just a single piece of material. Researchers inspired by soft robots have built a pumping artificial heart that could one day replace the real deal.
The team of Bioengineers at Cornell University build their robots out of a solid, plastic foam, which naturally has an interconnected network of tubes to let air flow – just as our muscles are permeated by blood vessels. A solid coating of plastic seals everything inside like a skin.
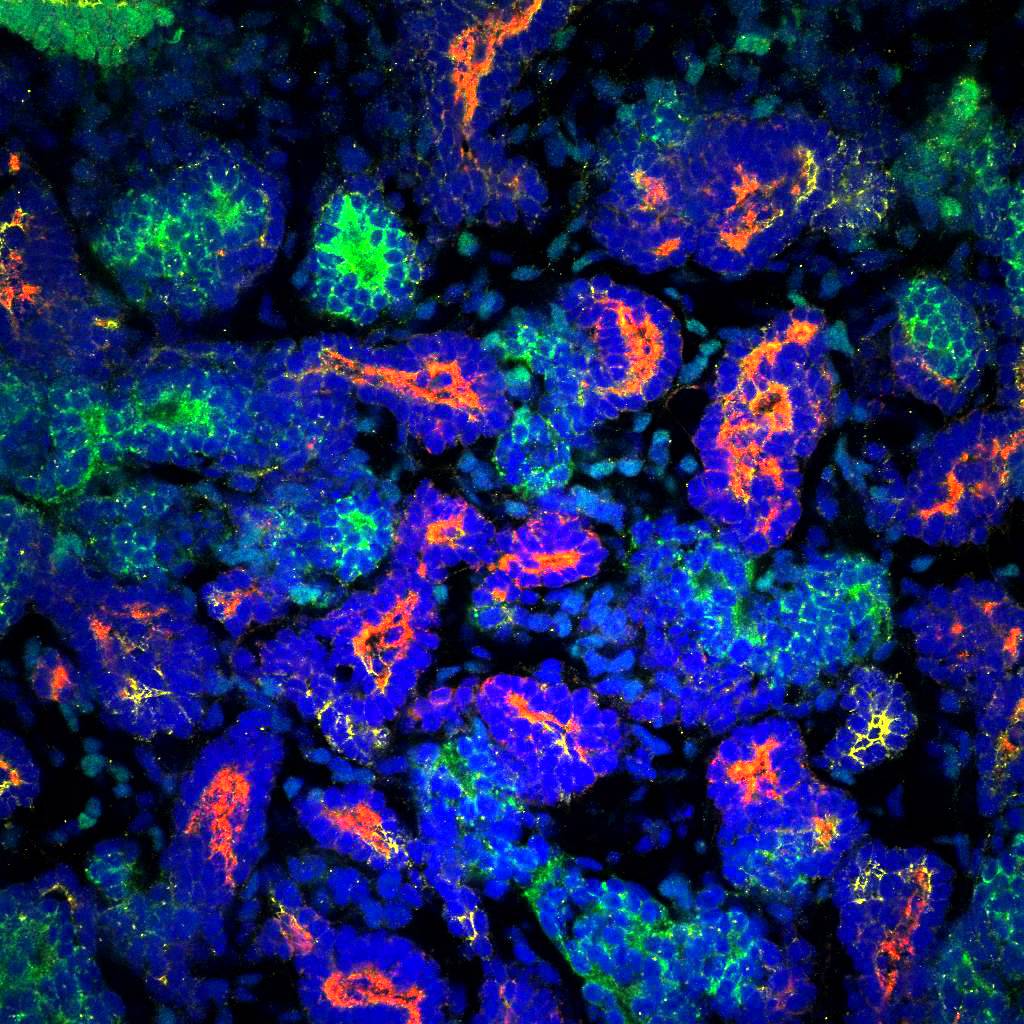
2) Researchers at QMUL have developed a way of assembling organic molecules into complex tubular tissue-like structures without the use of moulds or techniques like 3D printing. Self-assembling material can grow and change shape and one day could lead to artificial arteries.
The method uses solutions of peptide and protein molecules that, upon touching each other, self-assemble to form a dynamic tissue at the point at which they meet. As the material assembles itself it can be easily guided to grow into complex shapes.
This discovery could lead to the engineering of tissues like veins, arteries, or even the blood-brain barrier. The technique could also contribute to the creation of better implants, complex tissues, or more effective drug screening methods.
3) Neural Implant Enables Paralyzed ALS Patient to Type Six Words per Minute.
A massive collaboration of doctors and computer scientists gets one step closer to mind-controlled devices.
An eclectic team of researchers affiliated with BrainGate, a consortium of neuroscientists, engineers, computer scientists, and mathematicians, have published a study in Nature Medicine that profiles two subjects who control a cursor with their thoughts more deftly than previous systems allowed.
Earlier versions of the system allowed subjects to perform such tasks as drinking from a coffee thermos using a robotic arm, or playing simple games. The latest version brings finer control and ease of use. One participant was even able to type at a rate of six words a minute, using software originally developed to help people type type with eye movement.
4) Robots have many strong suits, but delicacy traditionally hasn’t been one of them. Rigid limbs and digits make it difficult for them to grasp, hold, and manipulate a range of everyday objects without dropping or crushing them. Now Soft robotic gripper can gently pick up and identify wide array of objects.
At a conference this month, researchers from Distributed Robotics Lab demonstrated a 3D-printed robotic hand made out of silicone rubber that can lift and handle objects as delicate as an egg and as thin as a compact disc.
Just as impressively, its three fingers have special sensors that can estimate the size and shape of an object accurately enough to identify it from a set of multiple items.
5) There’s a big ocean under the ice… NASA’s JPL team is working on a simple solution to get a sense of the deep ocean first: it’s working on the Buoyant Rover for Under-Ice Exploration. As you will see in the video, JPL tested it in choppy, methane-rich waters in Alaska.
TV Presenter: Olesya Yermakova @olesyayermakova.
Video: Vladimir Shlykov www.GetYourMedia.ru
Read more