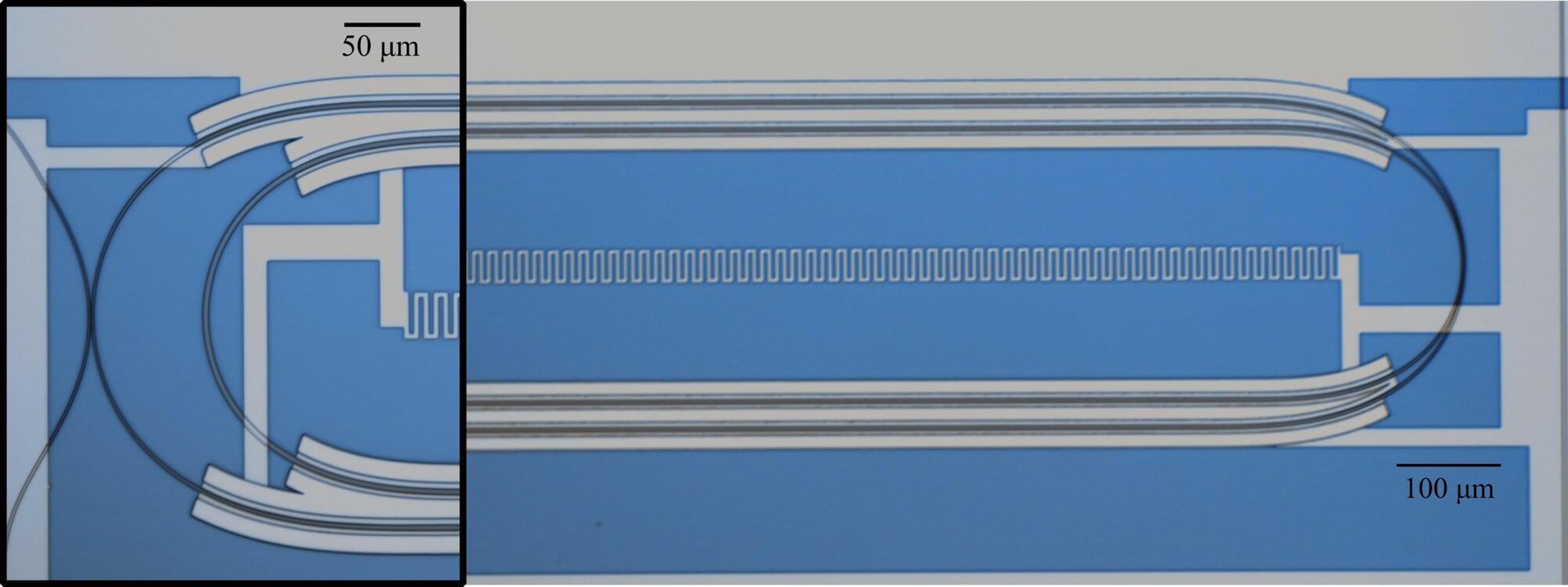
Applied physicists at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a photon router that could plug into quantum networks to create robust optical interfaces for noise-sensitive microwave quantum computers.
The breakthrough is a crucial step toward someday realizing modular, distributed quantum computing networks that leverage existing telecommunications infrastructure. Comprising millions of miles of optical fiber, today’s fiber-optic networks send information between computing clusters as pulses of light, or photons, all around the world in the blink of an eye.
Led by Marko Lončar, the Tiantsai Lin Professor of Electrical Engineering and Applied Physics at SEAS, the team has created a microwave-optical quantum transducer, a device designed for quantum processing systems that use superconducting microwave qubits as their smallest units of operation (analogous to the 1s and 0s of classical bits).