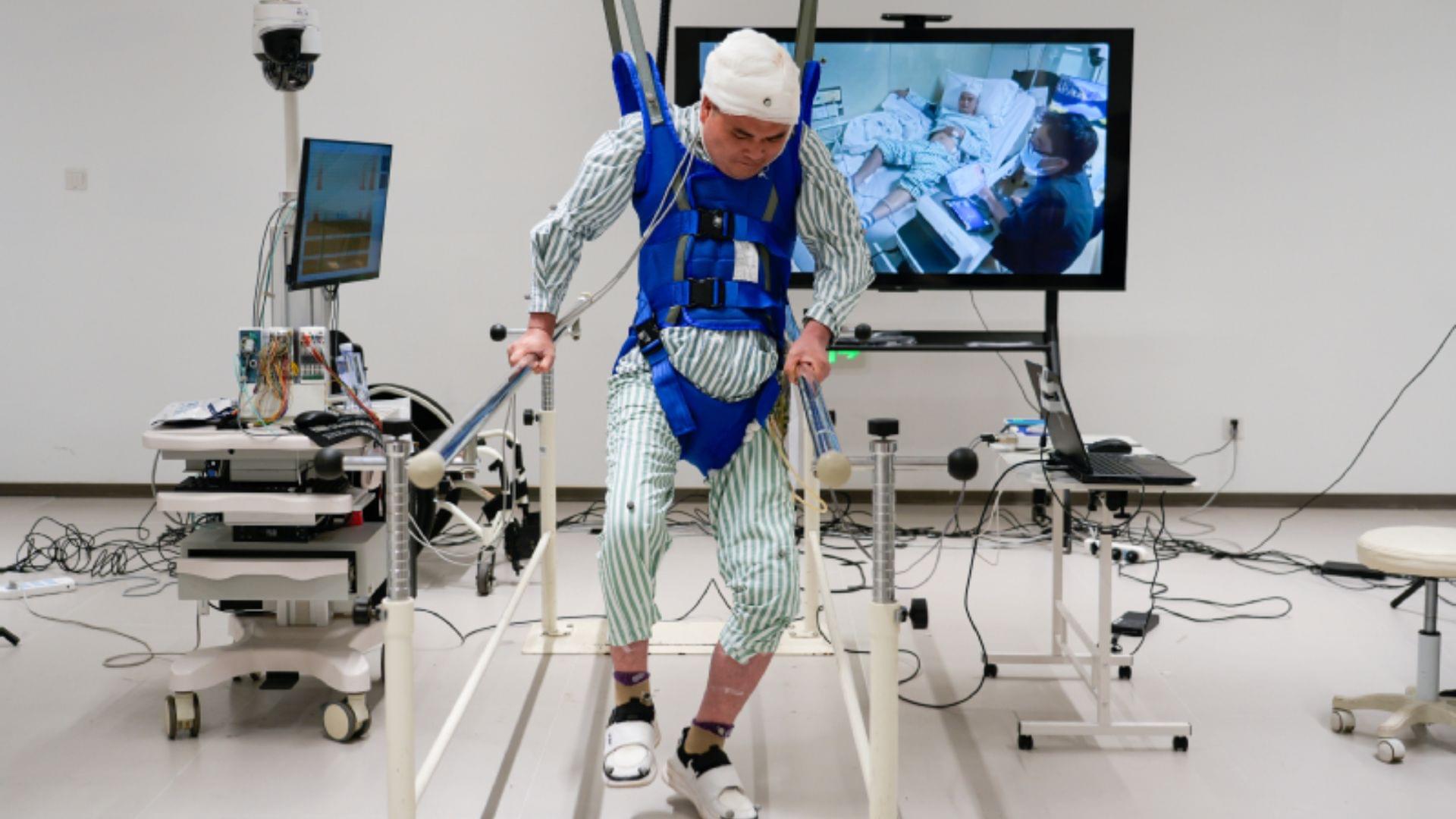
Paralyzed patients in China regained mobility within 24 hours of groundbreaking brain-spinal implant surgery.

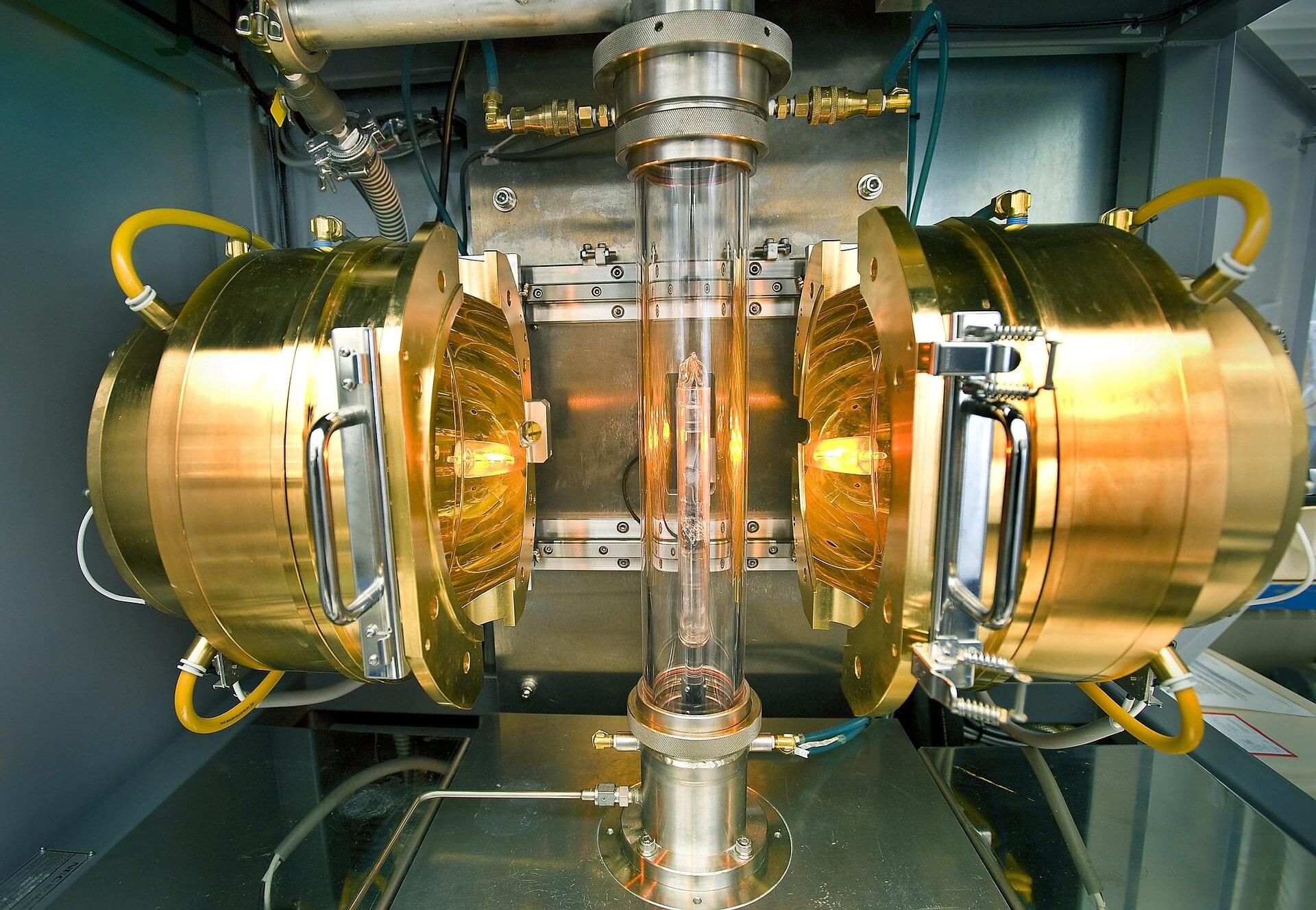
Scientists from the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) and collaborators have discovered a new way to control superconductivity—an essential phenomenon for developing more energy-efficient technologies and quantum computing—by simply twisting atomically thin layers within a layered device.
By adjusting the twist angle, they were able to finely tune the “superconducting gap,” which plays a key role in the behavior of these materials. The research is published in Nature Physics.
The superconducting gap is the energy threshold required to break apart Cooper pairs—bound electron pairs that enable superconductivity at low temperatures. Having a larger gap allows superconductivity to persist at higher, more accessible temperatures, and tuning the gap is also important for optimizing Cooper pair behavior at the nanoscale, contributing to the high functionality of quantum devices.
A team of researchers at Peking University claims to have made a breakthrough in chip technology, potentially reshaping the semiconductor race.
Their newly developed 2D transistor is said to be 40% faster than the latest 3-nanometre silicon chips from Intel and TSMC while consuming 10% less energy. This innovation, they say, could allow China to bypass the challenges of silicon-based chipmaking entirely.
“It is the fastest, most efficient transistor ever,” according to an official statement published last week on the PKU website.
Led by physical chemistry professor Peng Hailin, the research team believes their approach represents a fundamental shift in semiconductor technology.
Peking University researchers have developed a 2D transistor that operates 40% faster and uses 10% less energy than leading silicon chips.
Download Star Trek Fleet Command for FREE now here: https://bit.ly/3XYvSJ2 to support my channel, and enter the promo code VOYAGER30 to unlock Neelix, the morale officer from Voyager FREE.
Dr. Clément Vidal joins John Michael Godier to discuss his new paper on the Spider Stellar Engine, a hypothetical form of stellar propulsion using binary pulsar systems. The conversation explores how such systems could serve as **technosignatures**, the philosophy of post-biological civilizations, and the potential for advanced beings to manipulate entire stars or even create new universes.
Vidal, C. 2024. “The Spider Stellar Engine: A Fully Steerable Extraterrestrial Design?” Journal of the British Interplanetary Society 77 : 156–66. doi:10.59332/jbis-077–05-0156. https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.05038.
Vidal, C. 2019. “Pulsar Positioning System: A Quest for Evidence of Extraterrestrial Engineering.” International Journal of Astrobiology 18 : 213–34. doi:10.1017/S147355041700043X. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.03316.
Delahaye, J. P., and C. Vidal. 2018. “Organized Complexity: Is Big History a Big Computation?” American Philosophical Association Newsletter on Philosophy and Computers 17 : 49–54. http://arxiv.org/abs/1609.07111.
#EventHorizon #SETI #Technosignatures #Astrophysics #StellarEngines #FermiParadox #ExtraterrestrialLife #Pulsars #SpaceExploration #PhilosophyOfScience #cosmology.
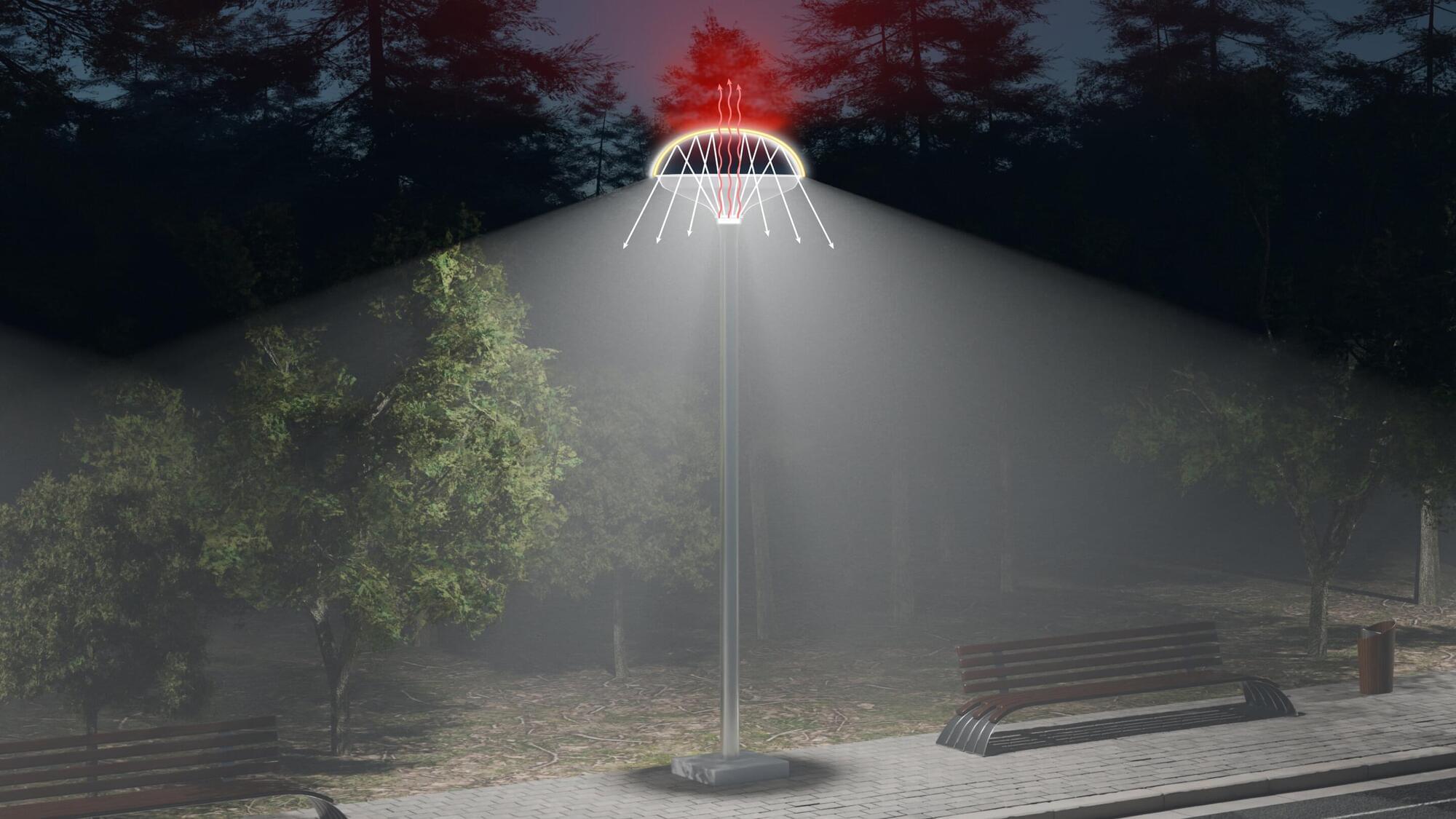



A new study resulting from a collaboration between King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) shows how nanomaterials can significantly reduce the carbon emissions of LED (light-emitting diode) streetlights. The research team estimates that by adopting this technology, the United States alone can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by more than one million metric tons.
The findings are published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
The nanomaterial, called nanoPE, enhances the emission of thermal radiation from the surface of the LED to reduce the LED temperature. LEDs generate heat, which raises their temperature and risks damaging the LED electronics and shortening the LED’s lifespan. In fact, approximately 75% of the input energy in LEDs is eventually lost as heat.

A study from Tübingen University and the German Center for Diabetes Research reveals that the brain plays a crucial role in obesity and type 2 diabetes development. It shows that even a brief period of consuming high-calorie processed foods can significantly alter brain insulin sensitivity, a key factor in weight gain and metabolic disorders. The research demonstrated that insulin’s appetite-suppressing effect in the brain diminishes after a short-term high-calorie diet, leading to insulin resistance. These effects were observed in healthy participants, suggesting that dietary habits could influence brain function before any significant weight gain occurs. Further research is needed to understand the brain’s role in these conditions.
The number of obese persons has grown significantly in recent decades, which presents significant difficulties for those who are impacted, healthcare systems, and those who provide treatment. The hormone insulin plays a key role in the development of obesity. Up until recently, there have been numerous signs indicating insulin causes neurodegenerative and metabolic disorders, especially in the brain. A recent study by the University Hospital of Tübingen, the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), and Helmholtz Munich offers intriguing new insights into the origins of type 2 diabetes and obesity as well as the brain’s function as a critical control center.
Obesity has only been officially recognized as a disease in Germany since 2020, despite the fact that it has long been known to cause a number of illnesses, including diabetes, heart attacks, and even cancer. The World Health Organization has already declared obesity to be an epidemic, affecting over one billion individuals globally and almost 16 million in Germany alone. A body mass index of 30 or more is considered obese, and a poor diet and insufficient exercise are frequently cited as the causes of this chronic illness. However, the mechanisms in the body that lead to obesity and cause the disease are more complex.
Obesity and the role of insulin in the brain
Unhealthy body fat distribution and chronic weight gain are linked to the brain’s sensitivity to insulin. What specific functions does insulin perform in the brain, and how does it affect individuals of normal weight? In their study, Prof. Dr. Stephanie Kullmann and her colleagues at the Tübingen University Hospital for Diabetology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology found the answer to this query. “Our findings demonstrate for the first time that even a brief consumption of highly processed, unhealthy foods (such as chocolate bars and potato chips) causes a significant alteration in the brain of healthy individuals, which may be the initial cause of obesity and type 2 diabetes,” says Prof. Kullmann, the study’s leader. In a healthy state, insulin has an appetite-suppressing effect in the brain. However, in people with obesity in particular, insulin no longer regulates eating behavior properly, resulting in insulin resistance.
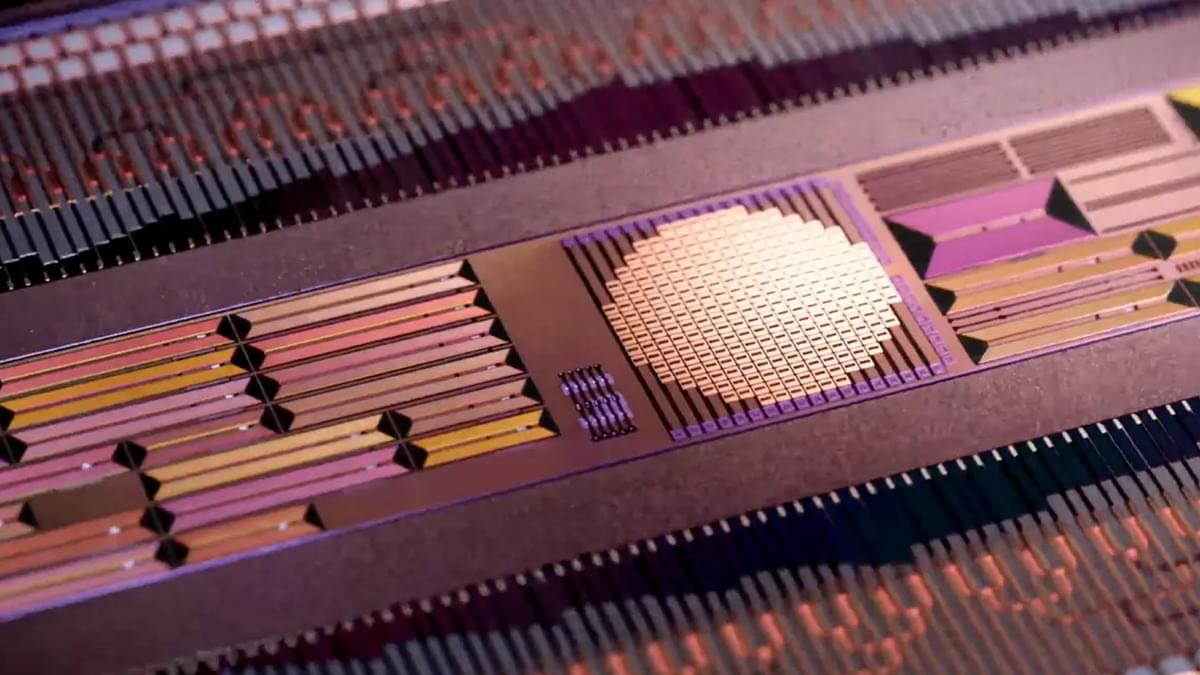

Scientists have unlocked a new way to control ionization, the process where atoms lose electrons, using specially designed light beams
By leveraging optical vortex beams, light that carries angular momentum, they can precisely dictate how electrons break free from atoms. This discovery could reshape imaging technology, enhance particle acceleration, and open doors to advancements in quantum computing.
Performing computation using quantum-mechanical phenomena such as superposition and entanglement.