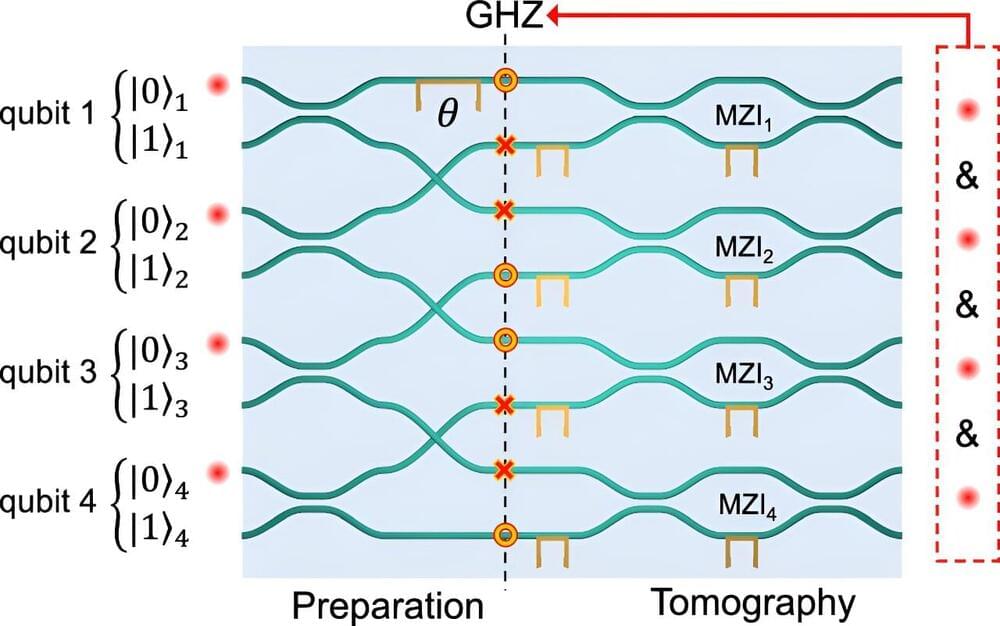
Wireless internet supports the daily activities of countless people worldwide, ranging from their professional communications to internet browsing and the streaming of movies or TV series. This spiking demand for wireless internet access goes hand in hand with greater power consumption, which in turn contributes to carbon emissions worldwide.
Future wireless networks should be able to support the high computational demands of many modern applications and internet services, while limiting power consumption. Some researchers have thus been developing energy efficient techniques supporting communication between devices and the sharing of media or other information online.
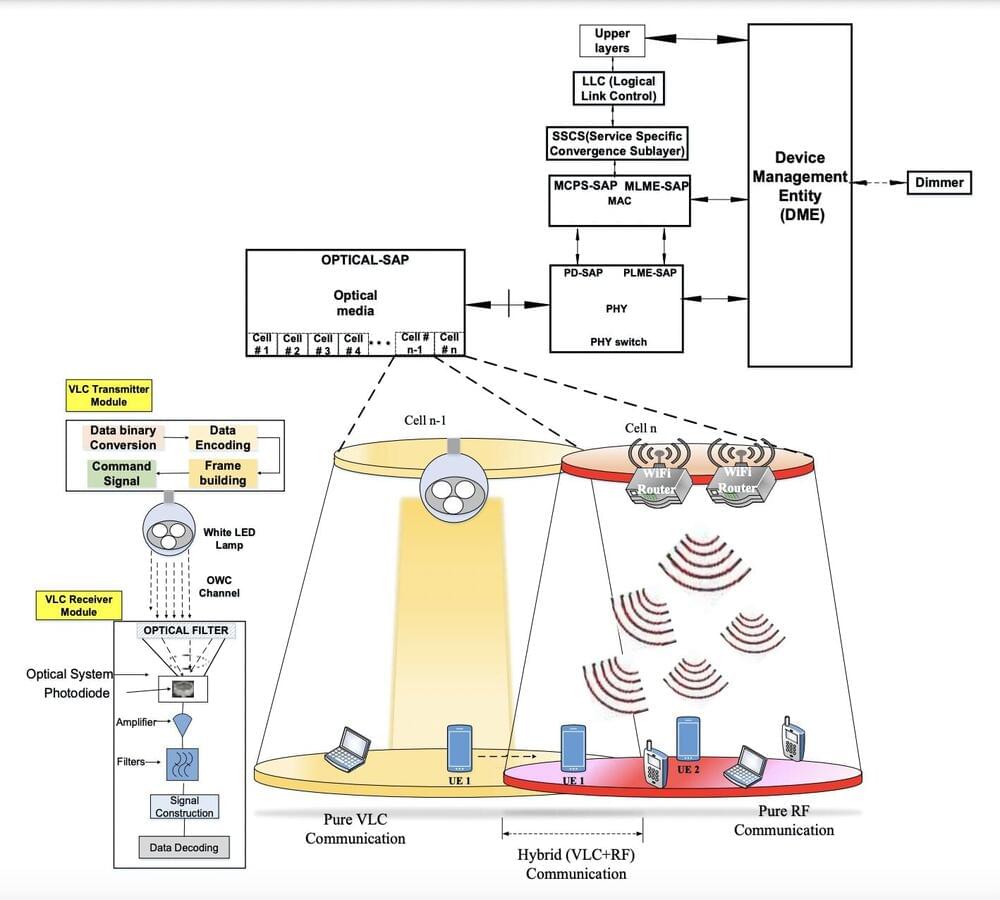
One of these solutions is known as visible light communication (VLC). This is a method to realize efficient wireless communication using visible light to transmit data, relying on light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or other artificial light sources.