Researchers from Colorado State University and the Colorado School of Mines have thought up a new computational imaging strategy that exploits the best of both the quantum and classical worlds. They developed an efficient and robust algorithm that fuses quantum and classical information for high-quality imaging. The results of their research were published Dec. 21 in Intelligent Computing.
Recently, the quantum properties of light have been exploited to enable super resolution microscopy. While quantum information brings new possibilities, it has its own set of limitations.
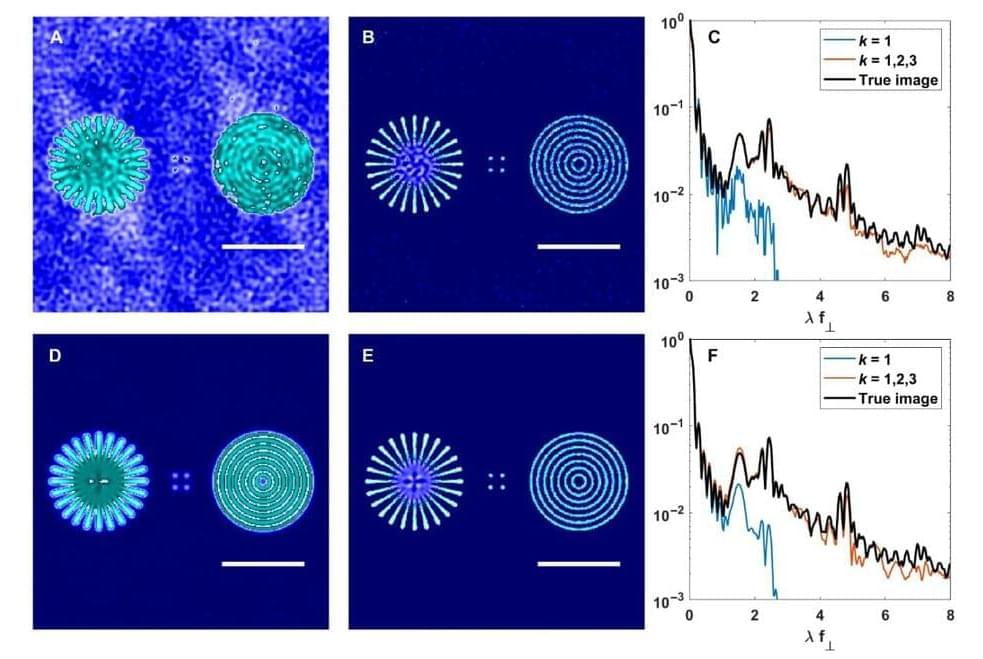
The researchers’ approach is based on classical and quantum correlation functions obtained from photon counts, which are collected from quantum emitters illuminated by spatiotemporally structured illumination. Photon counts are processed and converted into signals of increasing order, which contain increasing spatial frequency information. The higher spatial resolution information, however, suffers from a reduced signal-to-noise ratio at increasingly larger correlation orders.