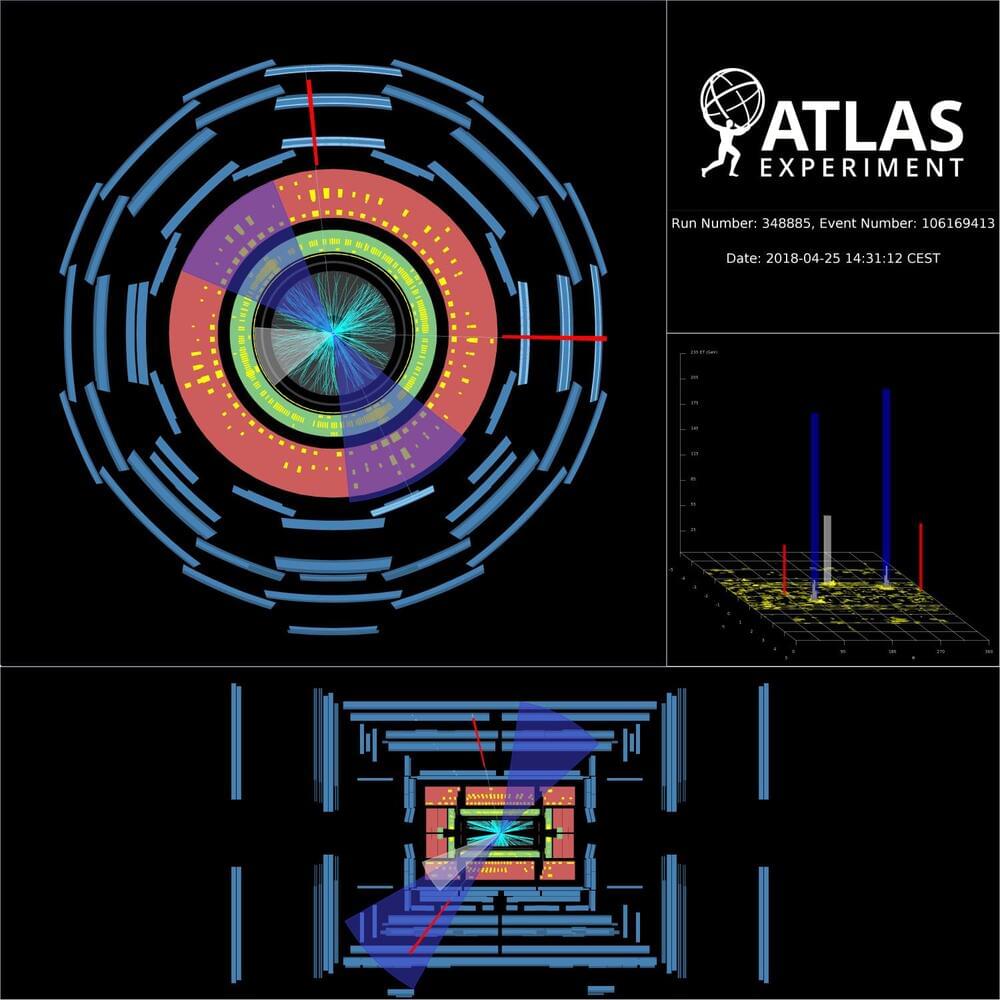
More than 40 years since its discovery, the Z boson remains a cornerstone of particle physics research. Through its production alongside heavy-flavour quarks (bottom and charm quarks), the Z boson provides a unique window into the internal dynamics of a proton’s constituents. Specifically, it allows researchers to probe the heavy-flavour contributions to “Parton Distribution Functions” (PDFs), which describe how a proton’s momentum is distributed among its constituent quarks and gluons. Using the full LHC Run-2 dataset, the ATLAS Collaboration measured Z boson production in association with both bottom (b) and charm © quarks, the latter for the first time in ATLAS. In their new result, physicists studied Z boson decays into electron or muon pairs produced in association with “jets” of particles. They focused on jets arising from the hadronisation of b or c quarks, creating two jet “flavours”: b-jets and c-jets. Physicists developed a new multivariate algorithm that was able to identify the jet-flavour, allowing them to measure the production of both Z+b-jets and Z+c-jets processes. Researchers then took this one step further and applied a specialised fit procedure, called the ‘flavour-fit’, to determine the large background contribution due to Z production together with other flavour jets. This method is driven by data and allows a precise description of the jet flavours for every studied observable. This led to a significant improvement in the precision of the results, allowing a more stringent comparison with theoretical predictions. The Z boson provides a unique window into the internal dynamics of a proton’s constituents. So, what did they find? ATLAS researchers measured the production rates (or “cross sections”) of several physics observables. These results were then compared with theoretical predictions, probing various approaches to describe the quark distributions in protons, the most recent computational improvements in QCD calculations and the effect of different treatments of the quark masses in the predictions. For example, Figure 1a shows the differential cross section for Z+1 b-jet production as a function of the transverse momentum of the most energetic b-jet in the event. Results show that predictions treating the b-quarks as massless (blue squares and red triangles) provide the best agreement with measurements. Z+2 b-jets angular observables are in general well understood, while some discrepancies with data appear in the invariant mass of the 2 b-jets, whose spectrum is not well modelled by the studied predictions. Figure 1: Measured fiducial cross-section as a function of a) leading b-jet pT for Z+b-jets events and b) leading c-jet x_F (its momentum along the beam axis relative to the initial proton momentum) for Z+c-jets events. Data (black) are compared with several theoretical predictions testing different theoretical flavour schemes, high order accuracy calculations and intrinsic charm models. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Studying Z+c-jets production offered a unique possibility to investigate the hypothesis of intrinsic (valence-like) components of c-quarks in the proton. With this result, the ATLAS Collaboration contributes to the long-standing debate on the existence of this phenomenon, currently supported by experimental measurements from the LHCb Collaboration. As shown in Figure 1b, the Z+c-jets results were compared with several hypotheses for intrinsic charm content. Due to the larger experimental and theoretical uncertainty on Z+c-jets processes, the current result makes no strong statement on the intrinsic c-quark component in the proton. However, it does improve physicists’ sensitivity to this effect, as the new data will be used in future by PDF fitting groups to set tighter constraints on the intrinsic charm distribution in the proton. Overall, the new ATLAS result provides deep insights for refining theoretical predictions, thereby fostering a deeper understanding of the dynamics of heavy-flavour quark content in the proton. About the event display: Display of a candidate Z boson decaying to two muons alongside two b-jets, recorded by the ATLAS detector at a centre-of-mass collision energy of 13 TeV. Blue cones indicate the b-jets, and the red lines indicate the muon tracks. Starting from the centre of the ATLAS detector, the reconstructed tracks of the charged particles in the inner detector are shown as cyan lines. The energy deposits in the electromagnetic (the green layer) and hadronic (the red layer) calorimeters are shown as yellow boxes. The hits in the muon spectrometer (the outer blue layer) are shown as light blue blocks. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Learn more Measurements of the production cross-section for a Z boson in association with b-or c-jets in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector (arXiv:2403.15093, see figures) Measurements of the production cross-section for a boson in association with in proton–proton collisions at 13 TeV (JHEP 7 (2020) 44, arXiv:2003.11960) LHCb Collaboration, Study of Z Bosons Produced in Association with Charm in the Forward Region (Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 (2022) 82,001, arXiv:2109.08084) See also the full list of ATLAS physics results.