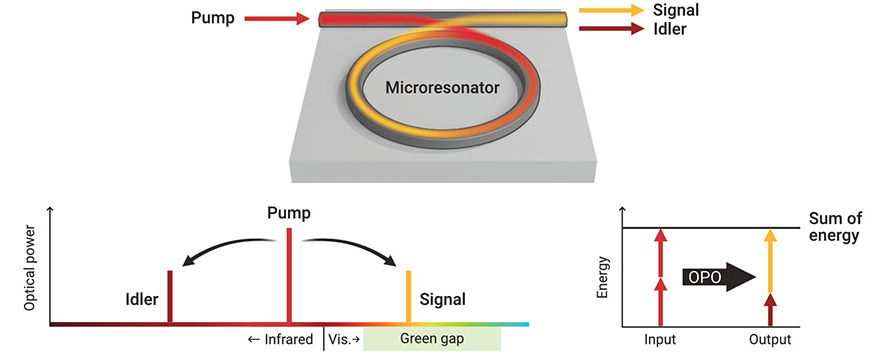
It’s not easy making green.
For years, scientists have fabricated small, high-quality lasers that generate red and blue light. However, the method they typically employ — injecting electric current into semiconductors — hasn’t worked as well in building tiny lasers that emit light at yellow and green wavelengths. Researchers refer to the dearth of stable, miniature lasers in this region of the visible-light spectrum as the “green gap.” Filling this gap opens new opportunities in underwater communications, medical treatments and more.
Compact laser diodes can emit infrared, red and blue wavelengths, but are highly inefficient at producing green and yellow wavelengths, a region known as the ‘green gap’. (Image: S. Kelley, NIST)