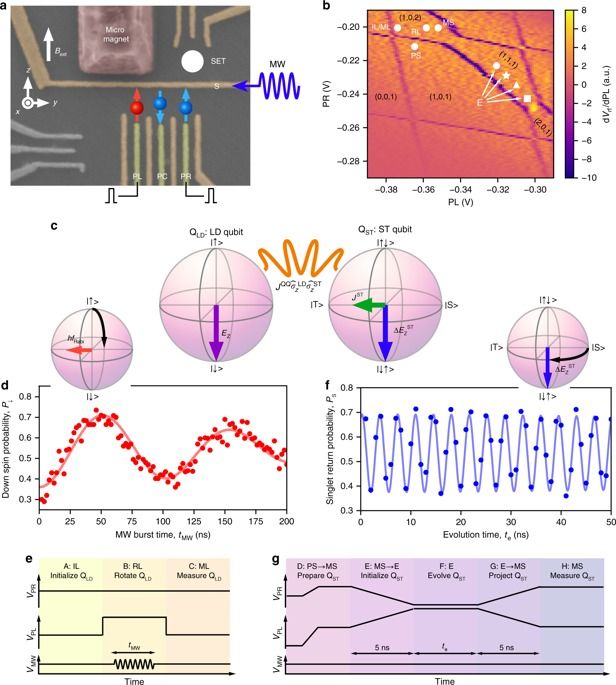
University of New South Wales researchers at the Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology (CQC2T) have shown for the first time that they can build atomic precision qubits in a 3D device — another major step towards a universal quantum computer.
The team of researchers, led by 2018 Australian of the Year and Director of CQC2T Professor Michelle Simmons, have demonstrated that they can extend their atomic qubit fabrication technique to multiple layers of a silicon crystal — achieving a critical component of the 3D chip architecture that they introduced to the world in 2015. This new research was published today in Nature Nanotechnology (“Spin read-out in atomic qubits in an all-epitaxial three-dimensional transistor”).