Lasers are everywhere nowadays: Doctors use them to correct eyesight, cashiers to scan your groceries, and quantum scientist to control qubits in the future quantum computer. For most applications, the current bulky, energy-inefficient lasers are fine, but quantum scientist work at extremely low temperatures and on very small scales. For over 40 years, they have been searching for efficient and precise microwave lasers that will not disturb the very cold environment in which quantum technology works.
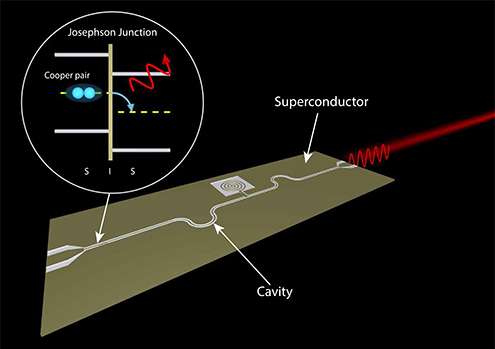
A team of researchers led by Leo Kouwenhoven at TU Delft has demonstrated an on-chip microwave laser based on a fundamental property of superconductivity, the ac Josephson effect. They embedded a small section of an interrupted superconductor, a Josephson junction, in a carefully engineered on-chip cavity. Such a device opens the door to many applications in which microwave radiation with minimal dissipation is key, for example in controlling qubits in a scalable quantum computer.
The scientists have published their work in Science on the 3rd of March.