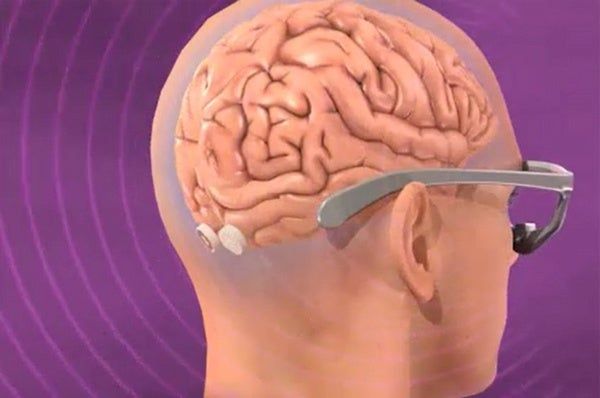
In normal vision, light falls on the retinas inside the eyes, and is immediately transduced into electrochemical signals before being uploaded to the brain through the optic nerves. So you do not see light itself, but the brain’s interpretation of electrochemical signals in the visual parts of the brain. It follows that, if your eyes do not work, but your brain is stimulated just so, your visual neurons will activate (and you will be able to see) just the same as if your eyes were in perfect condition.
Sounds easy, but can we do that? Building on decades of research in visual neuroscience, my lab, in collaboration with Susana Martinez-Conde’s, has now conducted some of the studies that validate this idea, completing some of the most important preliminary steps towards a new kind of visual prosthetic.
Francis Collins, the Director of the National Institutes of Health, has just posted a blog that highlights our approach. He took notice of our work when we first presented it at this year’s meeting for the Principal Investigators of the BRAIN Initiative—the NIH led government funding initiative meant to spur research along on topics like brain implants. The BRAIN Initiative funds several agencies including the NIH, including the National Science Foundation, who kindly funded the grant driving our research thus far.