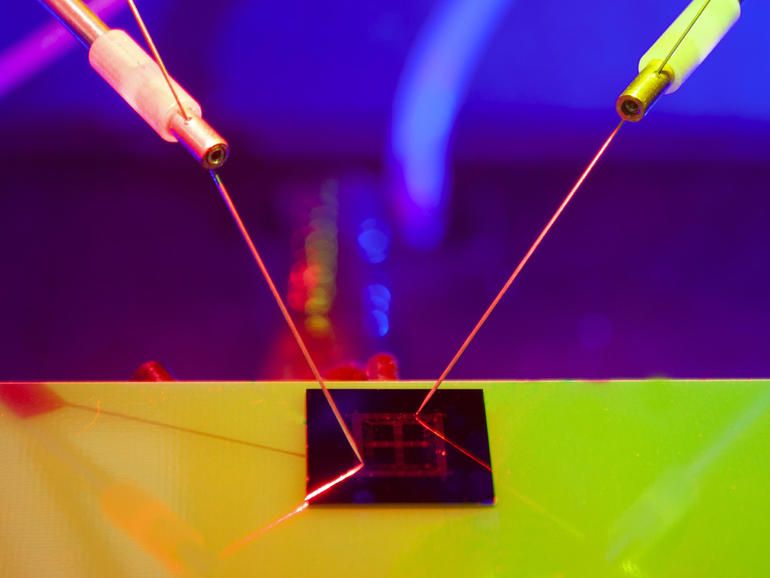
The chip could potentially be used to power drones, robotics, smart watches, and bionic implants.
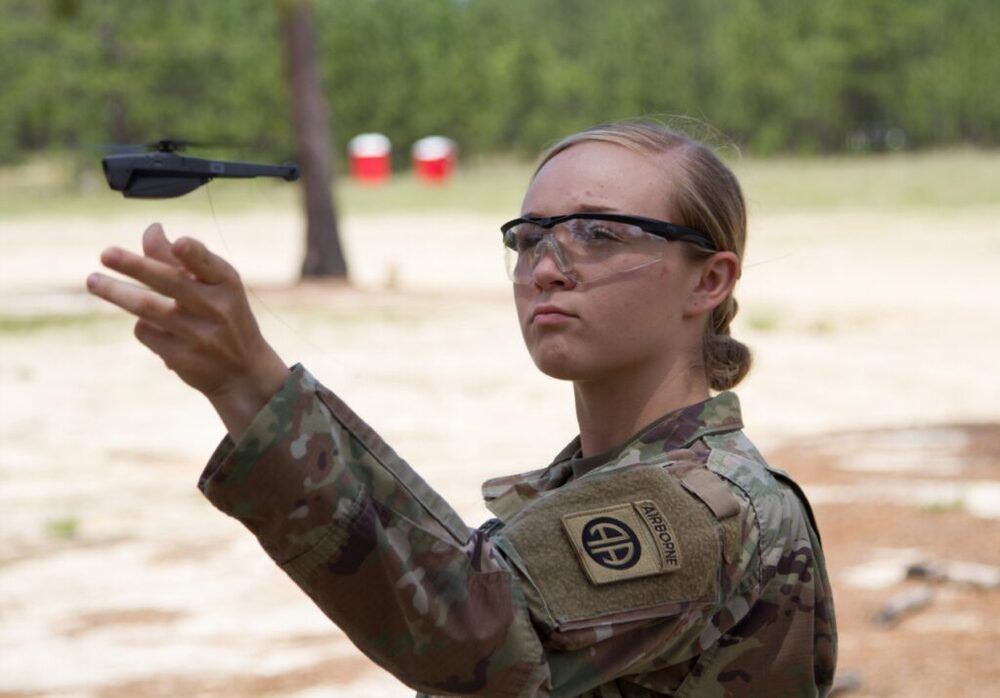



Its taking a bit more time for soldiers to adjust to their new drones.
Let Your Robots Off The Leash – Or Lose: AI Experts.
In DARPA-Army experiments, soldiers tried to micromanage their drones and ground robots, slowing their reaction times and restricting their tactics. Can AIs earn troops’ trust?
In 2019, Switzerland-based Flyability had a mystery to solve at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant. Was nuclear waste still present in one of the plant’s decommissioned reactors?
“At the time of the disaster, the fifth block of the Chernobyl Plant was under construction and nearing completion,” a Flyability spokesperson said. “Given the rush to leave, there was no record of whether the holding pools in Reactor Five had ever received the depleted uranium fuel bars for which they had been made.”
Fast forward 33 years – Chernobyl’s decommissioning team needed to know whether any nuclear waste remained in the reactor. Like a flying Sherlock Holmes, Flyability drones took the case.
This simple laser demonstration is actually a great crash course on how these anti-drone weapons work.
At first glance, this video is just a simple promotional video for Rafael’s Drone Dome, an anti-drone laser weapon. But at just two minutes long, it does a really excellent job at explaining what how a laser weapon actually takes down a drone.
VTOL (vertical take-off and landing) drones are quite versatile, as they combine the vertical flight of a helicopter with the fast and efficient forward flight of a fixed-wing airplane. This one features an extended range, thanks to a fuel cell power system.
The experimental aircraft was developed by a team at the Netherlands’ Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), working with colleagues from the Royal Netherlands Navy and the Netherlands Coastguard. It has a 3-meter wingspan (9.8 ft), weighs 13 kg (29 lb), and features 12 motor/propeller units distributed on its two wings. Even if several of the motors fail, it can reportedly still fly and land successfully.
The drone is also a “tail-sitter”-type VTOL. This means that when taking off and landing, its body is angled upwards, allowing the propellers to work more like a helicopter’s rotor blades. For going into forward flight, the thrust is electronically redistributed between the 12 motors, causing the aircraft to level out into a horizontal orientation.

Fido, meet F1d0.
Newly developed robotic K9s will soon be prowling Tyndall Air Force Base in Panama City, Florida, to enhance security and surveillance patrolling, WMBB-TV reported Monday.
The 325th Security Forces Squadron, which handles security for the base, said the robo-dogs are weatherproof, four-legged, unmanned patrolling drones that have two-way communication abilities and high-tech sensors that cost about $100,000 a pop, the outlet reported.


Drones will rule the battlefield. Until anti drone tech comes up to match it. I was picturing a anti drone system. One system that uses an old school radar anti aircraft gun, also equipped with a set of small missiles like the Iron Dome system, also equipped with some kind of laser weapon, and some kind of electro magnetic EMF weapon. All four in one package, that could engage multiple targets simultaneously. And, this will have to come standard, like SAM systems are now.
Azerbaijan used oil wealth to buy attack drones from Turkey and Israel. It was a huge advantage.