Legacy Method of Inheriting Assets
Many Bitcoin owners choose to use a custodial account, in which the private keys to a wallet are generated and controlled by their exchange—or even a bank or stock broker. In this case, funds are passed to heirs in the usual way. It works like this…
An executor, probate attorney, or someone with a legal claim contacts the organization that controls the assets. They present a death certificate, medical proxy or power-of-attorney. Just as with your bank account or stocks and bonds, you have the option of listing next of kin and the proportion of your assets that should be distributed to each. These custodial services routinely ask you to list individuals younger than you and alternate heirs, along with their street addresses, in the event that someone you list has died before you.
Of course, Bitcoin purists and Libertarians point out that the legacy method contradicts the whole point of owning a cryptocurrency. Fair enough.
Multisig to the Rescue
Using multisig would be far easier, if wallet vendors would conform to standards for compatibility and embed technology into hardware and software products. Unfortunately, they have been slow to do so, and there are not yet widely recognized standards to assure users that an implementation is both effective and secure. But, there is some good news: It’s fairly easy to process your ordinary account passwords and even the security questions with a roll-your-own multisig process. I’ve done it using PGP and also using Veracrypt—two widely recognized, open source encryption platforms.
This short article is not intended as an implementation tutorial, but if the wallet vendors don’t jump up to home plate, I may release a commercial tool for users to more easily add multisig to their wallets. It really is safe, simple and effective. (If readers wish to partner with me on this? I estimate that it will take $260,000 and about six months).
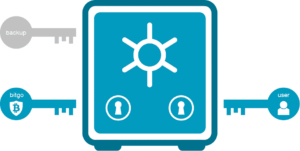
What is Multisig and How Does it Protect your Wealth?
Multisig allows anyone with credentials to an account, wallet or even a locked safe to create their own set of rules concerning which combinations of friends and relatives can access their assets without the original owner. The owner sets conditions concerning who, when, how much and which accounts can be accessed — and the heirs simply offer passwords or proof of identity. If implemented properly, it doesn’t matter if some of the heirs have forgotten passwords or died before the original owner.
This can be illustrated in an example. I am intentionally describing a complex scenario, so that you consider a full-blown implementation. Although the ‘rules’ listed below appear to be complex, the process for creating the associated passwords is trivial.
The last 2 rules listed below do not use Multisig technology, but rather Smart Contracts. It enhances an owner’s ability to dictate terms. Here, then, is the scenario…
I want heirs to have access to my assets
at banks, brokers, exchanges or other ac–
counts–but only under certain conditions:
- If any 4 of 11 trusted family and friends come together and combine their passwords (or an alternate proof-of-identity), they may access my wealth and transfer it to other accounts
- But, if one is my husband, Fred, or my daughter, Sue, then only two trusted individuals are needed
- —But not Fred and Sue together (At least one must be an outsider)
- If any account has less than $2500, then it goes to my favorite charity, rather than the individuals I have listed
- None of my accounts can be unlocked by my heirs, until I have not accessed them with my own password for 3 months. Prior to that, the Multisig will fail to gain access.
 Again, the decedent’s wishes are complex, but executing and enforcing these rules is trivial. In my presentations, I describe the method on two simple PowerPoint slides. Even that short description is sufficient to show anyone who has used common cryptography apps to weave their own multisig add-on.
Again, the decedent’s wishes are complex, but executing and enforcing these rules is trivial. In my presentations, I describe the method on two simple PowerPoint slides. Even that short description is sufficient to show anyone who has used common cryptography apps to weave their own multisig add-on.
Of course, each individual will need to locate their own secret password, but a biometric or other conforming proof-of-identity can be substituted. Even if several survivors cannot recall their credentials, the multisig method allows other combinations of individuals to access the assets across all accounts.
This article may leave you wondering about the legal process—and this is where I agree with the Libertarian viewpoint: Sure! The courts have a process and heirs should document their access and decisions for tax purposes and to assure each other of fair play. But a key benefit of cryptocurrency and the disintermediation offered by the blockchain is the personal empowerment of access with impunity and without waiting for any legal process.
Let the courts to what they do, while you honor the wishes of your dearly departed.
If this article generates sufficient interest, I may prepare a short tutorial on how to split off your own Multisig passwords, regardless of which wallet or hosted services you use. It will work with any vendor, app or gadget —or— Perhaps, I will refine my homespun solution and offer it as an add-on app that can be used with any wallet, bank account or exchange. Simple, ubiquitous and effective multisig should have been available to even traditional banking customers years ago!
Philip Raymond co-chairs CRYPSA, hosts the New York Bitcoin Event and presents at
Crypto Conferences around the world. Book a presentation or consulting engagement.





 So, what are the signs that an ICO is a scam? Is there anything you can do—short of hiring an expert—to evaluate each new proposal that comes along?
So, what are the signs that an ICO is a scam? Is there anything you can do—short of hiring an expert—to evaluate each new proposal that comes along?