This site is currently unavailable to visitors from the European Economic Area while we work to ensure your data is protected in accordance with applicable EU laws.



On his appointment, he said, It is really a great honour and privilege to be part of the Board of the Data Lab Scotland’s Artificial Intelligence and data to help contribute and provide strategic direction to the leadership of the Lab.
I am deeply humbled for this opportunity to contribute and help unlock the rich opportunities for AI and data, not just in Scotland, UK and across the world, by bringing industry, academia and public sector to harness opportunities, connect people and ideas, develop knowledge and expertise for the good of humanity and society-creating a better and sustainable economy and society.
The Nigerian-British man stressed his love for data and AI, saying, I am deeply passionate and intentional about data, AI, transformation, innovation, education, technology, inclusion, social and global mobility.

According to 81% of hospital CIOs surveyed by my company, security vulnerability is the leading pain point driving legacy data management decisions. That’s no surprise as healthcare continues to rank as one of the most cyber-attacked industries year over year. In a study by the Health Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS), 80% of healthcare organizations reported having legacy operating systems in place. Cybersecurity in healthcare is increasingly becoming a chronic condition.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), which measures risk to critical national infrastructure, says legacy software ranks as a dangerous “bad practice.” That’s because the use of unsupported or end-of-life legacy systems offers some of the easiest entry points for bad actors to gain access and cause havoc within a medical environment. With the average price tag for a healthcare data breach at an all-time high of $10.1 million, the overall cost to a breached organization is high in terms of economic loss and reputation repair.
To fortify defenses against cyberattacks, here are some tips for addressing out-of-production software in healthcare facilities.

AI is everywhere. Its use is being debated in headlines, on social media and around dinner tables. To some, the rate of AI acceleration is concerning, with many technology leaders calling for a six-month pause in the training of new systems to better understand the impact such tools are having. To others, AI is seen as the cornerstone of the fourth industrial revolution, the latest disruptive technology opening up possibilities for new ways of learning, working and living that we have never experienced before.
Yet, disruptive technologies are nothing new. They have been changing the way we live and work for decades. And these changes have not been without consequences, particularly in the form of economic dislocation and social upheaval. Automation in manufacturing has streamlined mass production and driven down costs; Ecommerce platforms have reshaped the way we shop and do business; even online education has found new ways to provide flexible and affordable ways of learning, delivering opportunities to millions across the globe that simply were not available before.
Presently, much of the discussion around the impact of AI is based on conjecture. However, it is widely agreed that it will have a major impact on jobs and even has the potential to call into question the very fundamentals of what work is. What is not understood is how AI will play out across society in the longer term. Will it, like previous technological revolutions, deliver short-term disruptions followed by long-term benefits, or will it be the catalyst for new ways of learning and upskilling and help reduce the widening digital divide?
Joscha Bach is a cognitive scientist focusing on cognitive architectures, consciousness, models of mental representation, emotion, motivation and sociality.
Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal.
Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
Twitter: https://twitter.com/TOEwithCurt.
Discord Invite: https://discord.com/invite/kBcnfNVwqs.
iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast/better-left-unsaid-wit…1521758802
Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b92xAErofYQA7bU4e.
Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: https://reddit.com/r/theoriesofeverything.
Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch.
0:00:00 Introduction.
0:00:17 Bach’s work ethic / daily routine.
0:01:35 What is your definition of truth?
0:04:41 Nature’s substratum is a “quantum graph”?
0:06:25 Mathematics as the descriptor of all language.
0:13:52 Why is constructivist mathematics “real”? What’s the definition of “real”?
0:17:06 What does it mean to “exist”? Does “pi” exist?
0:20:14 The mystery of something vs. nothing. Existence is the default.
0:21:11 Bach’s model vs. the multiverse.
0:26:51 Is the universe deterministic.
0:28:23 What determines the initial conditions, as well as the rules?
0:30:55 What is time? Is time fundamental?
0:34:21 What’s the optimal algorithm for finding truth?
0:40:40 Are the fundamental laws of physics ultimately “simple”?
0:50:17 The relationship between art and the artist’s cost function.
0:54:02 Ideas are stories, being directed by intuitions.
0:58:00 Society has a minimal role in training your intuitions.
0:59:24 Why does art benefit from a repressive government?
1:04:01 A market case for civil rights.
1:06:40 Fascism vs communism.
1:10:50 Bach’s “control / attention / reflective recall” model.
1:13:32 What’s more fundamental… Consciousness or attention?
1:16:02 The Chinese Room Experiment.
1:25:22 Is understanding predicated on consciousness?
1:26:22 Integrated Information Theory of consciousness (IIT)
1:30:15 Donald Hoffman’s theory of consciousness.
1:32:40 Douglas Hofstadter’s “strange loop” theory of consciousness.
1:34:10 Holonomic Brain theory of consciousness.
1:34:42 Daniel Dennett’s theory of consciousness.
1:36:57 Sensorimotor theory of consciousness (embodied cognition)
1:44:39 What is intelligence?
1:45:08 Intelligence vs. consciousness.
1:46:36 Where does Free Will come into play, in Bach’s model?
1:48:46 The opposite of free will can lead to, or feel like, addiction.
1:51:48 Changing your identity to effectively live forever.
1:59:13 Depersonalization disorder as a result of conceiving of your “self” as illusory.
2:02:25 Dealing with a fear of loss of control.
2:05:00 What about heart and conscience?
2:07:28 How to test / falsify Bach’s model of consciousness.
2:13:46 How has Bach’s model changed in the past few years?
2:14:41 Why Bach doesn’t practice Lucid Dreaming anymore.
2:15:33 Dreams and GAN’s (a machine learning framework)
2:18:08 If dreams are for helping us learn, why don’t we consciously remember our dreams.
2:19:58 Are dreams “real”? Is all of reality a dream?
2:20:39 How do you practically change your experience to be most positive / helpful?
2:23:56 What’s more important than survival? What’s worth dying for?
2:28:27 Bach’s identity.
2:29:44 Is there anything objectively wrong with hating humanity?
2:30:31 Practical Platonism.
2:33:00 What “God” is.
2:36:24 Gods are as real as you, Bach claims.
2:37:44 What “prayer” is, and why it works.
2:41:06 Our society has lost its future and thus our culture.
2:43:24 What does Bach disagree with Jordan Peterson about?
2:47:16 The millennials are the first generation that’s authoritarian since WW2
2:48:31 Bach’s views on the “social justice” movement.
2:51:29 Universal Basic Income as an answer to social inequality, or General Artificial Intelligence?
2:57:39 Nested hierarchy of “I“s (the conflicts within ourselves)
2:59:22 In the USA, innovation is “cheating” (for the most part)
3:02:27 Activists are usually operating on false information.
3:03:04 Bach’s Marxist roots and lessons to his former self.
3:08:45 BONUS BIT: On societies problems.
Subscribe if you want more conversations on Theories of Everything, Consciousness, Free Will, God, and the mathematics / physics of each.
I’m producing an imminent documentary Better Left Unsaid http://betterleftunsaidfilm.com on the topic of “when does the left go too far?” Visit that site if you’d like to contribute to getting the film distributed (in 2020) and seeing more conversations like this.
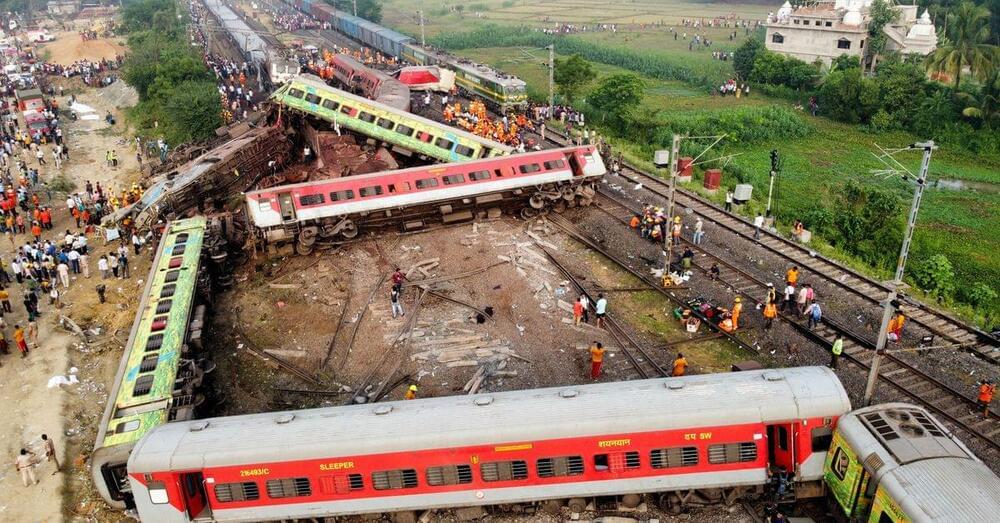

Long considered the lifeline of the world’s most populous country, the 170-year-old system has seen rapid expansion and modernisation under Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s push to boost infrastructure and connectivity in the fast-growing economy.
This year, the government made a record 2.4-trillion-rupee ($30 billion) capital outlay for the railways, a 50% increase over the previous fiscal year, to upgrade tracks, ease congestion and add new trains.
A new, semi-high-speed train built in India and called the “Vande Bharat Express”, or “Salute to India Express”, is showcased as evidence of this modernisation, with Modi himself flagging off the first journeys of many of the trains around the country.
Overcoming AI Technophobia
Currently, there is a public surge of interest in AI topics, especially in Large Language Models, like ChatGPT. This is not a random development.
AI is here to stay and will have huge social and economic implications, seen as both a blessing and a curse. In view of its potential dangers, many AI scientists have expressed concern over AI developments that border on technophobia. But there is a means of defending ourselves from the dark side of AI as expressed in dystopian science fiction.


The U.S.-China decoupling is giving rise to a divided tech landscape between the two major economies, shaping the development of the red-hot area of generative AI, which turns text into various forms of content like prose, images, and videos.
China, in order to reduce dependence on the U.S. technological foundation, has been pursuing its own large language models that match OpenAI’s GPT models. But unlike the U.S., some of its most advanced AI endeavors are happening at established internet juggernauts, such as Baidu.
The search engine and autonomous driving giant rolled out its counterpart to ChatGPT in March. Now the 23-year-old firm wants to have a stake in other AI startups, too. The company aims to have a stake in other AI startups. During a JPMorgan summit in China this week, Baidu’s co-founder and CEO Robin Li announced the launch of a billion yuan ($145 million) fund to back generative AI companies.

Is this Mars thing really happening? SpaceX did its first test launch of Starship this spring, the rocket that it’s developing to send to Mars. But getting to Mars is still a long way off. So does SpaceX have the funding and business plan to pull it off?For sponsor-free episodes of The Indicator from Planet Money, subscribe to Planet Money+ via Apple Podcasts or at plus.npr.org.