A study of a guaranteed income program in Stockton, California, found that after receiving an extra $500 in cash each month for a year, recipients had better job prospects and improved mental health.
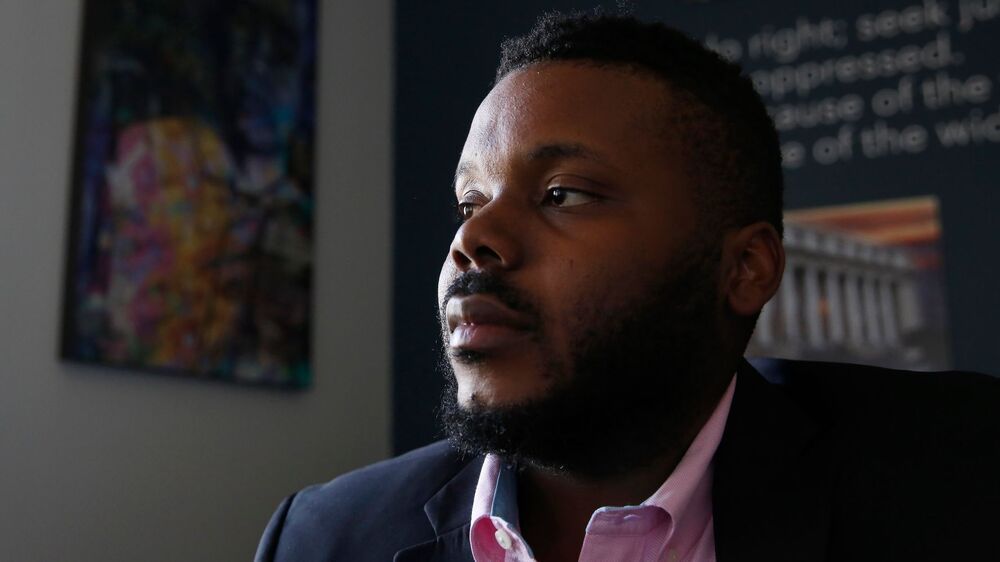
As part of the Stockton Economic Empowerment Demonstration (SEED) pilot program, 125 people in the California city received $500 per month for 24 months starting in February 2019. The program, initiated by former Mayor Michael Tubbs, chose recipients in neighborhoods at or below the city’s median household income of $46033. The money, in prepaid debit cards, was unconditional, meaning people could spend it as they chose.
A study released Wednesday based on the first year of the project, from February 2019 to February 2020, found that beneficiaries got full-time jobs at over twice the rate of non-recipients, were less anxious and depressed over time, and reported improvements in emotional health, well-being and fatigue.