Superior energy density could see 621 miles of emissions-free motoring.


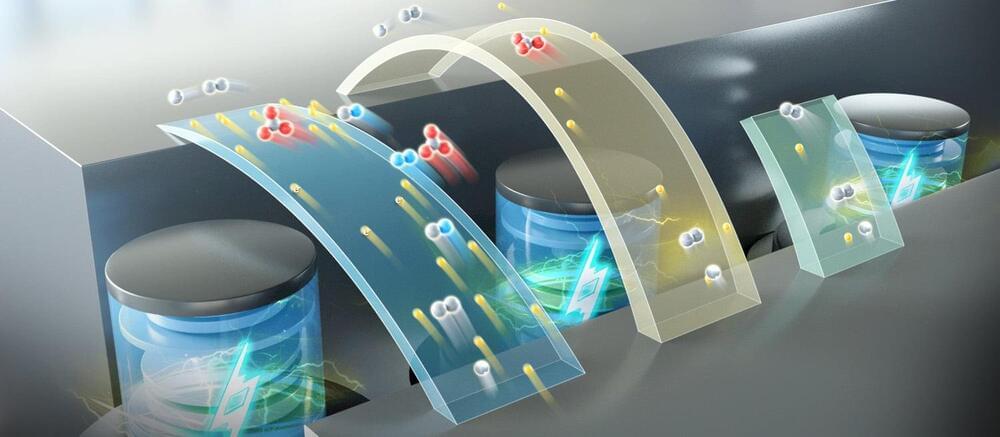
Traditional lithium-ion batteries, while offering high energy density, have compromised safety because they use flammable organic electrolytes.
Aqueous batteries use water as the solvent for electrolytes, significantly enhancing the safety of the batteries. However, due to the limited solubility of the electrolyte and low battery voltage, aqueous batteries typically have a lower energy density. This means that the amount of electricity stored per unit volume of aqueous battery is relatively low.
In a new study published in Nature Energy, a research group led by Prof. Li Xianfeng from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. Fu Qiang’s group also from DICP, developed a multi-electron transfer cathode based on bromine and iodine, realizing a specific capacity of more than 840 Ah/L, and achieving an energy density of up to 1,200 Wh/L based on catholyte in full battery testing.

Their findings “may expand aqueous battery applications in the power battery field”, said corresponding author Li Xianfeng, a professor at the CAS Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, who was quoted in a statement from the academy.
Lithium batteries are the standard used across the world because of their high energy density. Traditional lithium batteries contained a non-aqueous electrolyte – a component that allowed the battery to charge and discharge – which was flammable, the paper said.
Aqueous batteries are made up of a water-based electrolyte which does not present the same safety risks.

As well as slashing travel time to neighboring planets, PPR promises to support the transport of much heavier spacecraft, which can benefit from shielding against galactic cosmic rays, allowing space travelers to spend longer periods outside Earth’s protective dome.
The latter will be the subject of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) study, which is focusing on a large, heavily shielded ship to transport humans and cargo to Mars for the development of a Martian base.
“The main topics included: assessing the neutronics of the system, designing the spacecraft, power system, and necessary subsystems, analyzing the magnetic nozzle capabilities, and determining trajectories and benefits of the PPR. Phase II will build upon these assessments and further the PPR concept,” NASA said.

A process to dissolve the mineral olivine in acid could provide a plentiful, energy-efficient material for carbon-negative cement.
UK startup is set to develop innovative waterless hydro energy storage system, addressing limitations of traditional hydro power.

The main cost of an electric vehicle (EV) is its battery. The high cost of energy-dense batteries has meant EVs have long been more expensive than their fossil fuel equivalents.
But this could change faster than we thought. The world’s largest maker of batteries for electric cars, China’s CATL, claims it will slash the cost of its batteries by up to 50% this year, as a price war kicks off with the second largest maker in China, BYD subsidiary FinDreams.
What’s behind this? After the electric vehicle industry experienced a huge surge in 2022, it has hit headwinds. It ramped up faster than demand, triggering efforts to cut costs.

Scientific and technical research in the United States has led to decades of progress in energy efficiency, as we have seen on previous occasions. However, we have just learned of a breakthrough that was only theorized until now, finally, it has been put into operation. This is the first-ever reverse microwave, which cools food instead of heating it. Could you simply imagine that?
A reverse microwave is an innovative appliance that rapidly cools food and drinks without using electricity. Unlike a traditional microwave oven which uses microwave radiation to heat items, a reverse microwave utilizes thermoelectric cooling.
This technology allows the reverse microwave to draw heat away from the contents inside, lowering their temperature in just minutes. The concept behind reverse microwaves has existed for decades, but the technology is only now becoming available for home use in the United States.
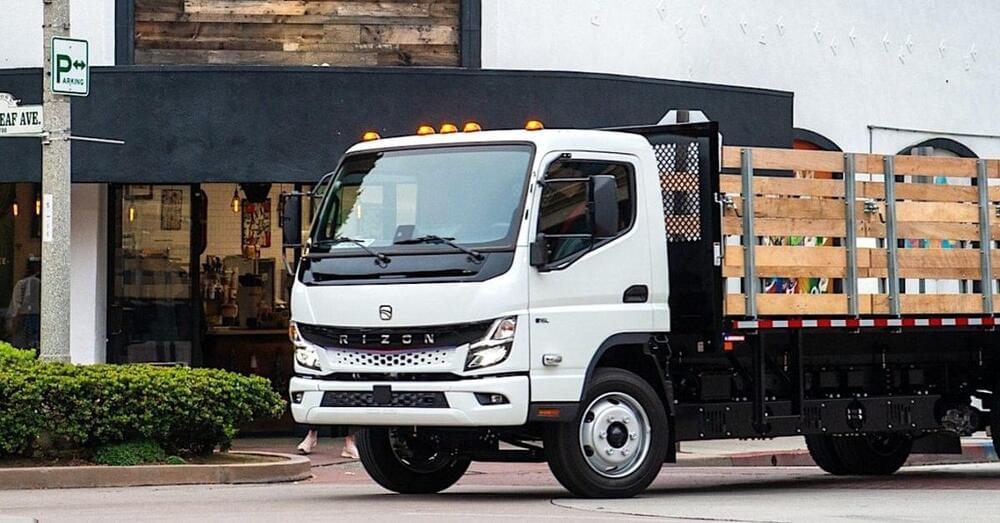

Daimler’s new, all-electric truck brand made its Canadian debut this week with the official market launch of its battery electric class 4 and 5 medium duty work trucks.
After making its North American debut at the 2023 ACT Expo in Anaheim, California, Daimler Truck’s RIZON brand has continued on a steady march towards production with initial preorders set to open this June. But it won’t just be Americans who can order a new RIZON electric box truck – Canadians will be able to add them to their fleets at the same time.
“Canada is very advanced regarding green energy and infrastructure and is a natural next step for RIZON’s second market,” explains Andreas Deuschle, the Global Head of RIZON. “We are very happy to bring our zero-emission solution to Canadian customers. They are proven OEM trucks with the latest technology from Daimler Truck.”