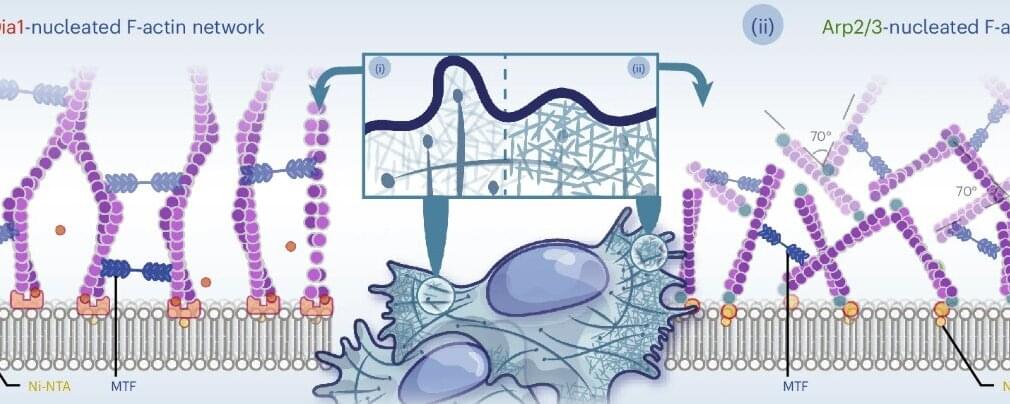
Prof. Michael Murrell’s group (lead author Zachary Gao Sun, graduate student in physics) in collaboration with Prof. Garegin Papoian’s group from the University of Maryland at College Park has found critical phenomena (self-organized criticality) that are reminiscent of the earthquakes and avalanches inside the cell cytoskeleton through self-organization of purified protein components.
In a groundbreaking discovery, researchers have found that the cell’s cytoskeleton—the mechanical machinery of the cell—behaves much like Earth’s crust, constantly regulating how it dissipates energy and transmits information. This self-regulating behavior enables cells to carry out complex processes such as migration and division with remarkable precision.
Even more striking, the study draws parallels between the behavior of microscopic cellular structures and massive celestial bodies, suggesting that the principles of criticality—where systems naturally tune themselves to the brink of transformation—may be universal across vastly different scales of nature.