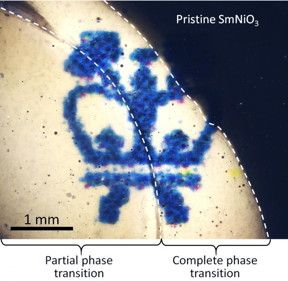
Abstract: Columbia Engineers discover that samarium nickelate shows promise for active photonic devices — SmNiO3 could potentially transform optoelectronic technologies, including smart windows, infrared camouflage, and optical communications.
A team led by Nanfang Yu, assistant professor of applied physics at Columbia Engineering, has discovered a new phase-transition optical material and demonstrated novel devices that dynamically control light over a much broader wavelength range and with larger modulation amplitude than what has currently been possible. The team, including researchers from Purdue, Harvard, Drexel, and Brookhaven National Laboratory, found that samarium nickelate (SmNiO3) can be electrically tuned continuously between a transparent and an opaque state over an unprecedented broad range of spectrum from the blue in the visible (wavelength of 400 nm) to the thermal radiation spectrum in the mid-infrared (wavelength of a few tens of micrometers). The study, which is the first investigation of the optical properties of SmNiO3 and the first demonstration of the material in photonic device applications, is published online today in Advanced Materials.
“The performance of SmNiO3 is record-breaking in terms of the magnitude and wavelength range of optical tuning,” Yu says. “There is hardly any other material that offers such a combination of properties that are highly desirable for optoelectronic devices. The reversible tuning between the transparent and opaque states is based on electron doping at room temperature, and potentially very fast, which opens up a wide range of exciting applications, such as ‘smart windows’ for dynamic and complete control of sunlight, variable thermal emissivity coatings for infrared camouflage and radiative temperature control, optical modulators, and optical memory devices.”