History tells us that games are an inseparable facet of humanity, and mainly for good reasons. Advocates of video games laud their pros: they help develop problem-solving skills, socialize, relieve stress, and exercise the mind and body—all at the same time! However, games also have a dark side: the potential for addiction. The explosive growth of the video game industry has spawned all sorts of games targeting different groups of people. This includes digital adaptations of popular board games like chess, but also extends to gambling-type games like online casinos and betting on horse races. While virtually all engaging forms of entertainment lend themselves to addictive behavior under specific circumstances, some video games are more commonly associated with addiction than others. But what exactly makes these games so potentially addictive?
This is a difficult question to answer because it deals directly with aspects of the human mind, and the inner workings of the mind are mostly a mystery. However, there may be a way to answer it by leveraging what we do know about the physical world and its laws. At the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), Japan, Professor Hiroyuki Iida and colleagues have been pioneering a methodology called “motion in mind” that could help us understand what draws us towards games and makes us want to keep reaching for the console.
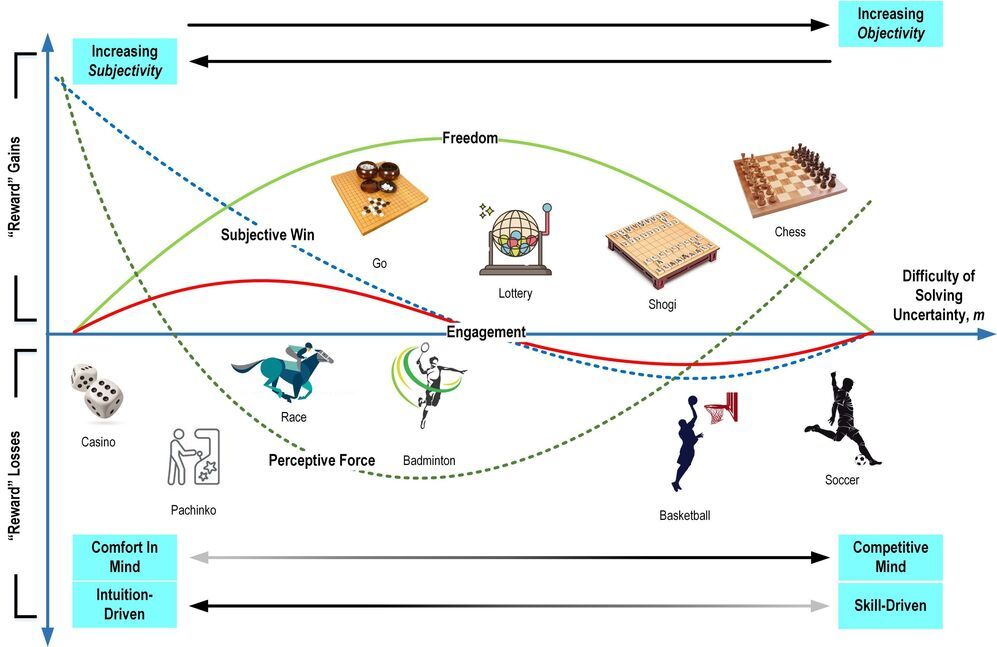
Their approach is centered around modeling the underlying mechanisms that operate in the mind when playing games through an analogy with actual physical models of motion. For example, the concepts of potential energy, forces, and momentum from classical mechanics are considered to be analogous to objective and/or subjective game-related aspects, including pacing of the game, randomness, and fairness. In their latest study published in IEEE Access, Professor Iida and Assistant Professor Mohd Nor Akmal Khalid, also from JAIST, linked their “motion in mind” model with the concepts of engagement and addiction in various types of games from the perceived experience of the player and their behaviors.