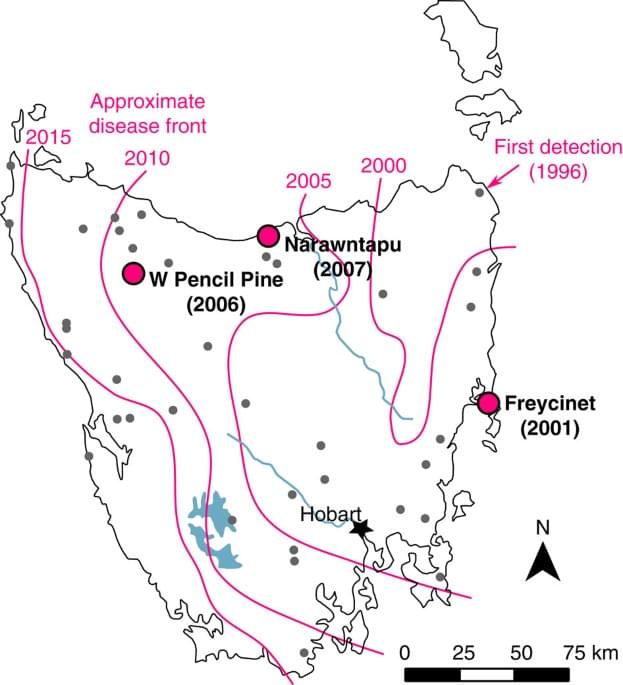
This finding “proved” the significance of chromosomal rearrangement, a crucial evolutionary indicator of the emergence of a new species.
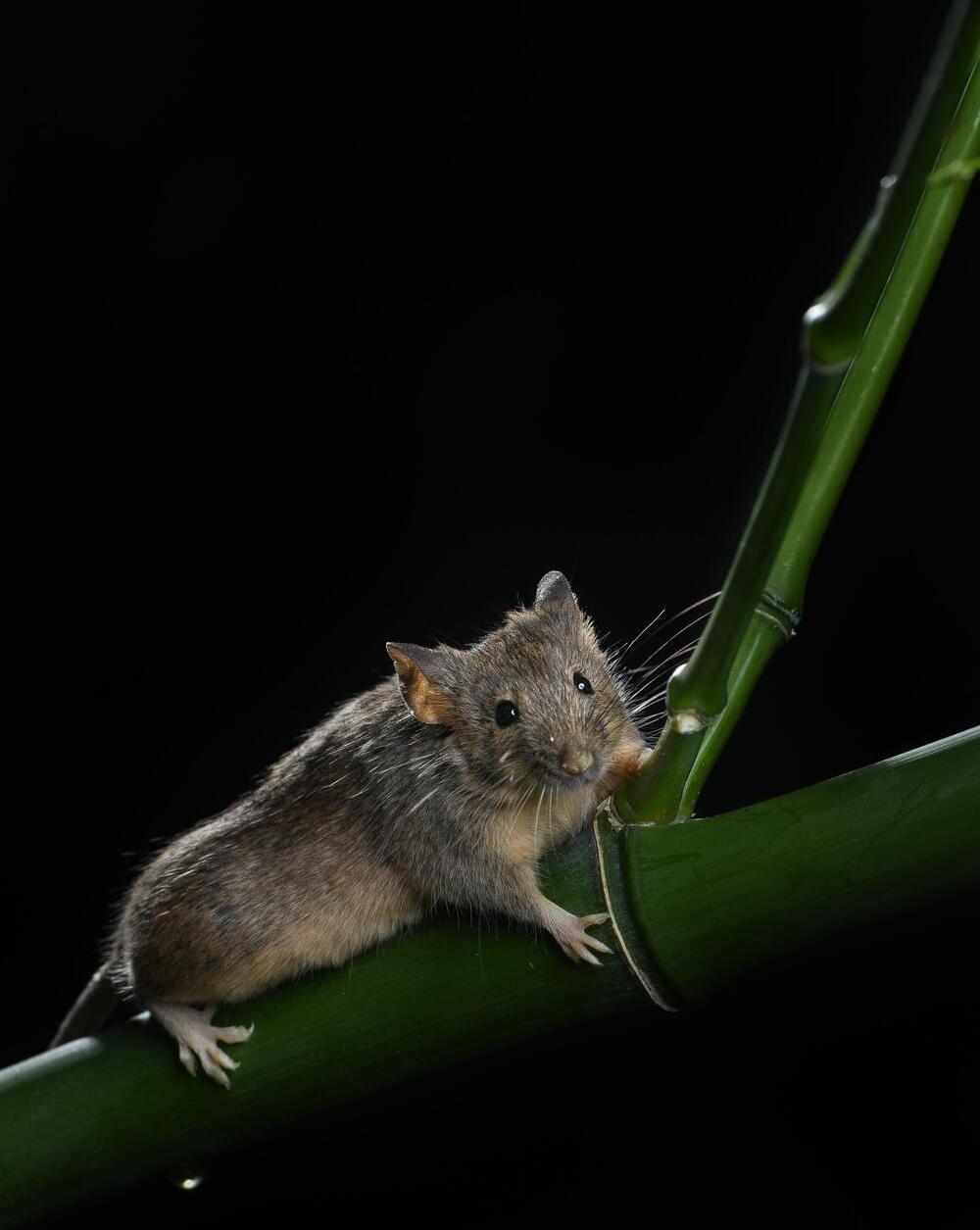
Researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) claim to have found a novel technique for programmable chromosome fusion successfully producing mice with genetic changes “that occur on a million-year evolutionary scale” in the laboratory.
The findings could shed light on how chromosome rearrangements—the tidy packages of organized genes provided in equal numbers by each parent, which align and trade or blend traits to produce offspring—influence evolution, reported Phys.org on Thursday.
Evolutionary chromosomal changes may take a million years in nature, but researchers are now reporting a novel technique enabling programmable chromosome fusion that has successfully produced mice with genetic changes that occur on a million-year evolutionary scale in the laboratory. The result may provide critical insights into how rearrangements of chromosomes—the tidy packages of organized genes, provided in equal number from each parent, which align and trade or blend traits to produce offspring—influence evolution.
In results published today in Science, the researchers reveal that chromosome-level engineering can be achieved in mammals, and they successfully derived a laboratory house mouse with novel and sustainable karyotype, providing critical insight into how chromosomal rearrangements may influence evolution.
“The laboratory house mouse has maintained a standard 40-chromosome karyotype—or the full picture of an organism’s chromosomes—after more than 100 years of artificial breeding,” said co-first author Li Zhikun, researcher in the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Institute of Zoology and the State Key Laboratory of Stem Cell and Reproductive Biology. “Over longer time scales, however, karyotype changes caused by chromosome rearrangements are common. Rodents have 3.2 to 3.5 rearrangements per million years, whereas primates have 1.6.”