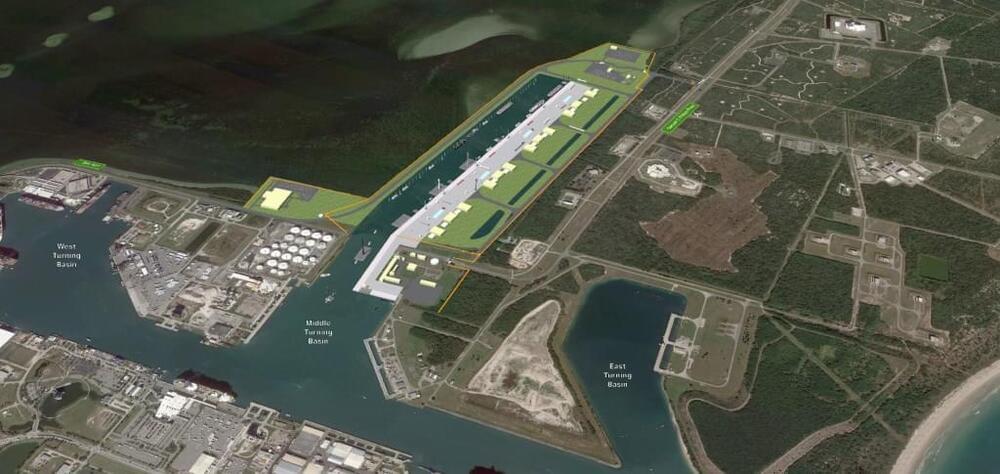
More Space Coast rocket launches mean a crowded fleet of support ships are already pushing Port Canaveral’s limits. So the state commissioned a study that suggests a $2.1 billion solution to give companies such as SpaceX and Blue Origin dedicated places to dock.
Space Florida, the state’s aerospace finance and development authority, released Thursday the Florida Spaceport System Maritime Intermodal Transportation Study that’s been in the works for more than a year.
“It was really important for us to make sure we had every stakeholder input throughout the process,” said Space Florida president and CEO Rob Long.