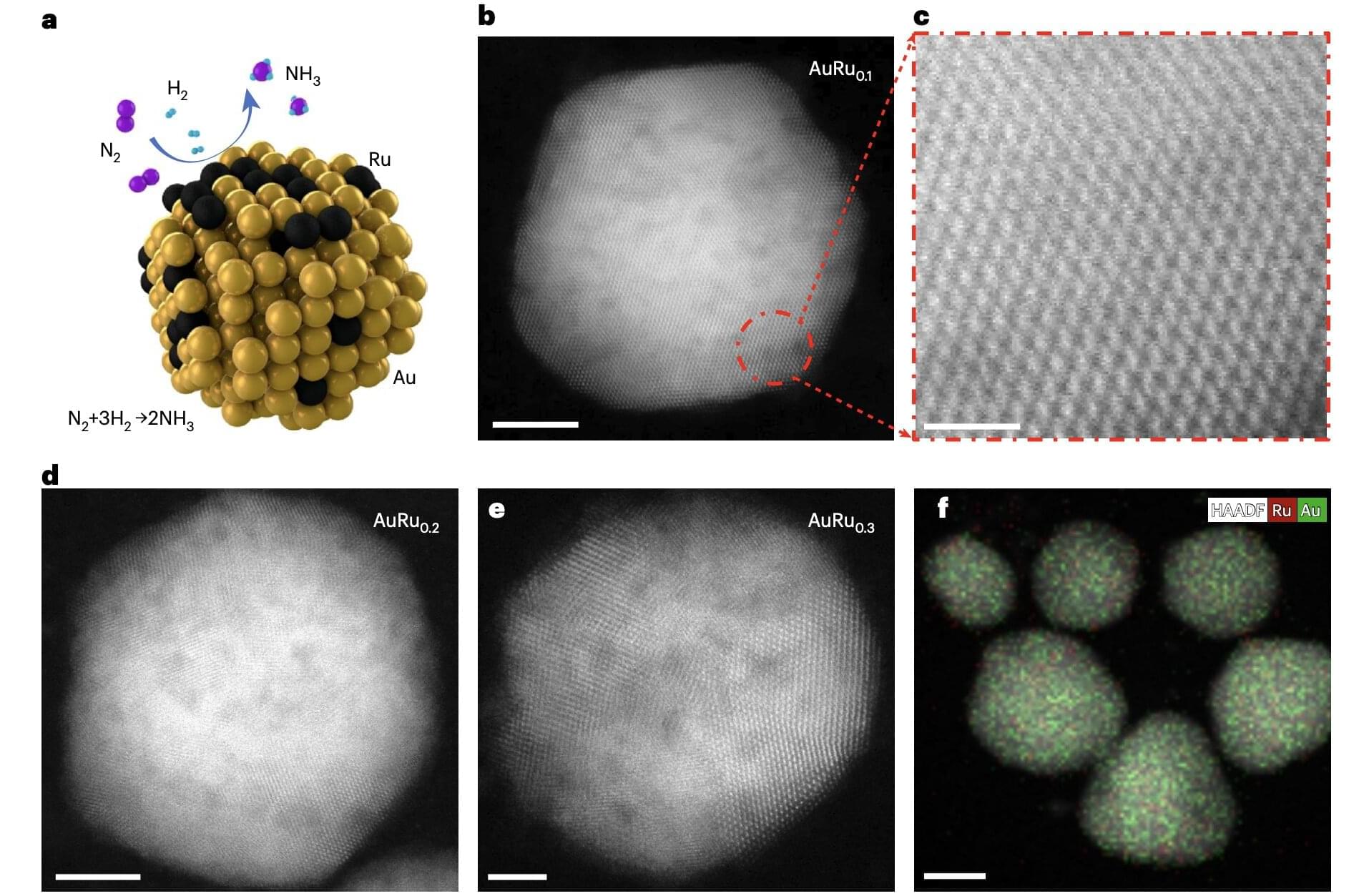
Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless chemical compound comprised of nitrogen and hydrogen that is widely used in agriculture and in industrial settings. Among other things, it is used to produce fertilizers, as well as cleaning products and explosives.
Currently, ammonia is primarily produced via the so-called Haber-Bosch process, an industrial technique that entails prompting a reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen at very high temperatures and pressure. Despite its widespread use, this process is known to be highly energy-intensive and is estimated to be responsible for approximately 3% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
Researchers at Stanford University School of Engineering, Boston College and other institutes have identified new promising catalysts (i.e., materials that speed up chemical reactions) that could enable the sunlight-driven synthesis of ammonia at room temperature and under normal atmospheric pressure.