DNA combined with the study of family history has been used to solve high-profile cold cases such as the Golden State Killer. Now, volunteers are using the technique to identify crime victims.



In the future, we may have to deal with biological weapons that target specific groups of people, passing over everyone else.
That’s according to a new report out of Cambridge University’s Centre for the Study of Existential Risk reviewed by The Telegraph. In it, the Cambridge researchers argue that world governments have failed to prepare for futuristic weapons based on advanced technology like artificial intelligence and genetic manipulation — or even a killer pathogen designed to kill only people of a particular race.

Faculty engaged in microbiome research across campus have previously shown that our microbiome plays a key role in defining human health. For example, microbial dysfunction in the infant gut – characterized by the enrichment of particular microbial genes and their products – drive immune dysfunction and can be used to predict the development of allergy and asthma in childhood. Perturbed microbial ecosystems across the human body have been linked to autoimmune disease, metabolic syndromes such as obesity and diabetes, skin diseases, and even multiple sclerosis. Gut microbes can even contribute to metabolizing drugs and influence how much enters the circulation.
Leveraging this expertise and collaborations with UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals in Oakland and San Francisco and institutions nationwide, the UCSF Benioff Center for Microbiome Medicine aims to develop a holistic understanding of our earliest interactions with microbes in utero, through birth, and in early life. These efforts aim to find ways of predicting and preventing not only asthma and allergy, but other childhood diseases – including dermatological, gastrointestinal, respiratory and neurological disorders.
“At the same time that we are developing therapeutic strategies to restore microbial ecosystems once they have been damaged,” Lynch said. “We also need to find ways to intervene in at-risk populations in very early life to prevent chronic diseases before they start.”
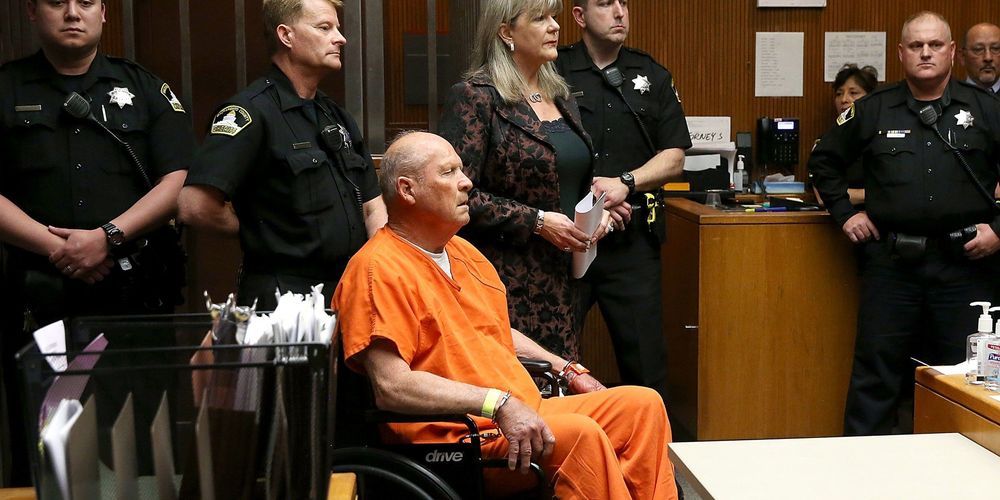
Three hundred and sixty-six days ago, CeCe Moore woke up to the headline that would change her world: “Suspected Golden State Killer, East Area Rapist Arrested After Eluding Authorities for Decades.” Later that day, those authorities would hold a press conference in front of the Sacramento County District Attorney’s office to explain how, a day earlier, they had finally put handcuffs on the man believed to have committed a series of sadistic rapes and murders that spread terror through California for more than 40 years. But Moore didn’t have to tune in to know how they had done it. “I knew immediately they had cracked it with genetic genealogy and GEDmatch,” she says.
She knew it because at the time, Moore was working as the genetic genealogy researcher on the PBS show Finding Your Roots and had a consulting business helping adoptees find their biological parents. To aid her searches, she regularly logged on to GEDmatch, a public database where hobbyists upload results from consumer genetic testing companies like 23andMe and Ancestry to find relatives with shared DNA and to reverse-engineer their family trees. It had come to her attention that another genealogist on the site, Barbara Rae-Venter, had been uploading files that seemed out of place, and Moore suspected they came not from family members, but from crime scenes. But she had never imagined that one of them belonged to the man believed to be one of the most notorious serial killers in US history. “This was going to be huge,” she remembers telling people that day.
But not even Moore could have predicted just how huge it would become. In the year since the dramatic arrest of Joseph James DeAngelo, the alleged Golden State Killer, investigative genetic genealogy has emerged as the most powerful new crime-fighting tool since DNA itself. The technique has been used to identify suspects in more than 50 additional cases. Its vast potential to crack tens of thousands more has given rise to a lucrative new forensic science business, the formation of dedicated family-tree-building police units, and the first-ever home DNA kit marketing campaign to get people to send in their spit to solve crimes.
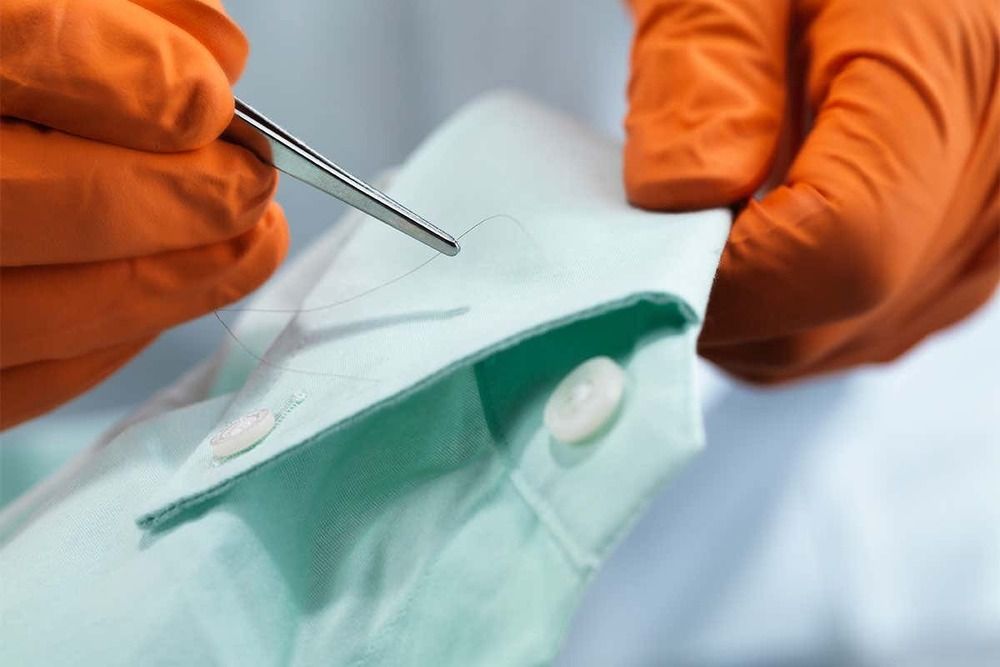
By Chelsea Whyte
Policing power may be about to get much stronger, thanks to another advance in genetic analysis. A new technique can link the patchy, limited DNA information held in forensic databases to the rich DNA libraries held by family tree-building websites, raising further questions about genetic privacy.
Earlier this year, an ancestry database used by people looking to trace their family history was used to identify the suspected Golden State Killer, a serial killer active in California decades ago. Since his arrest in April, genealogy databases – which allow consumers to upload their DNA sequences – have been used to crack several other cold cases.
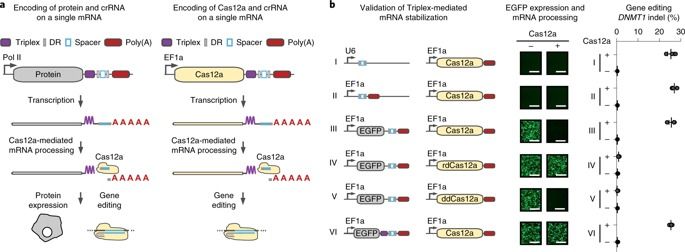
The ability to modify multiple genetic elements simultaneously would help to elucidate and control the gene interactions and networks underlying complex cellular functions. However, current genome engineering technologies are limited in both the number and the type of perturbations that can be performed simultaneously. Here, we demonstrate that both Cas12a and a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) array can be encoded in a single transcript by adding a stabilizer tertiary RNA structure. By leveraging this system, we illustrate constitutive, conditional, inducible, orthogonal and multiplexed genome engineering of endogenous targets using up to 25 individual CRISPR RNAs delivered on a single plasmid. Our method provides a powerful platform to investigate and orchestrate the sophisticated genetic programs underlying complex cell behaviors.
Today the U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced a comprehensive policy framework for the development and oversight of regenerative medicine products, including novel cellular therapies.
The framework — outlined in a suite of four guidance documents — builds upon the FDA’s existing risk-based regulatory approach to more clearly describe what products are regulated as drugs, devices, and/or biological products. Further, two of the guidance documents propose an efficient, science-based process for helping to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these therapies, while supporting development in this area. The suite of guidance documents also defines a risk-based framework for how the FDA intends to focus its enforcement actions against those products that raise potential significant safety concerns. This modern framework is intended to balance the agency’s commitment to safety with mechanisms to drive further advances in regenerative medicine so innovators can bring new, effective therapies to patients as quickly and safely as possible. The policy also delivers on important provisions of the 21st Century Cures Act.
We’re at the beginning of a paradigm change in medicine with the promise of being able to facilitate regeneration of parts of the human body, where cells and tissues can be engineered to grow healthy, functional organs to replace diseased ones; new genes can be introduced into the body to combat disease; and adult stem cells can generate replacements for cells that are lost to injury or disease. This is no longer the stuff of science fiction. This is the practical promise of modern applications of regenerative medicine.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful approach for integrated analysis of the rapidly growing volume of multi-omics data, including many research and clinical tasks such as prediction of disease risk and identification of potential therapeutic targets. However, the potential for AI to facilitate the identification of factors contributing to human exceptional health and life span and their translation into novel interventions for enhancing health and life span has not yet been realized. As researchers on aging acquire large scale data both in human cohorts and model organisms, emerging opportunities exist for the application of AI approaches to untangle the complex physiologic process(es) that modulate health and life span. It is expected that efficient and novel data mining tools that could unravel molecular mechanisms and causal pathways associated with exceptional health and life span could accelerate the discovery of novel therapeutics for healthy aging. Keeping this in mind, the National Institute on Aging (NIA) convened an interdisciplinary workshop titled “Contributions of Artificial Intelligence to Research on Determinants and Modulation of Health Span and Life Span” in August 2018. The workshop involved experts in the fields of aging, comparative biology, cardiology, cancer, and computational science/AI who brainstormed ideas on how AI can be leveraged for the analyses of large-scale data sets from human epidemiological studies and animal/model organisms to close the current knowledge gaps in processes that drive exceptional life and health span. This report summarizes the discussions and recommendations from the workshop on future application of AI approaches to advance our understanding of human health and life span.
Aging is often described as the outcome of interactions among genetic, environmental and lifestyle factors with wide variation in life and health span between and within species (Newman and Murabito, 2013; Partridge et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2019). Exceptional life and health span represents an extreme phenotype characterized by exceptional survival (well-beyond average life expectancy), delayed onset of age-related diseases (before 80 years of age) (Pignolo, 2019) and/or preservation of good health/function relative to their peers (Perls et al., 2000, 2002; Kaeberlein, 2018). The identification of SNP associations with exceptional life and health span is a starting point for identifying targets for interventions that could potentially promote healthy human aging.

The pursuit of longevity has been the goal of humanity since ancient times. Genetic alterations have been demonstrated to affect lifespan. As increasing numbers of pro-longevity genes and anti-longevity genes have been discovered in Drosophila, screening for functionally important genes among the large number of genes has become difficult. The aim of the present study was to explore critical genes and pathways affecting longevity in Drosophila melanogaster. In this study, 168 genes associated with longevity in D. melanogaster were collected from the Human Ageing Genomic Resources (HAGR) database. Network clustering analysis, network topological analysis, and pathway analysis were integrated to identify key genes and pathways. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was applied to verify the expression of genes in representative pathways and of predicted genes derived from the gene–gene sub-network. Our results revealed that six key pathways might be associated with longevity, including the longevity-regulating pathway, the peroxisome pathway, the mTOR-signalling pathway, the FOXO-signalling pathway, the AGE-RAGE-signalling pathway in diabetic complications, and the TGF-beta-signalling pathway. Moreover, the results revealed that six key genes in representative pathways, including Cat, Ry, S6k, Sod, Tor, and Tsc1, and the predicted genes Jra, Kay, and Rheb exhibited significant expression changes in ageing D. melanogaster strain w1118 compared to young ones. Overall, our results revealed that six pathways and six key genes might play pivotal roles in regulating longevity, and three interacting genes might be implicated in longevity. The results will not only provide new insight into the mechanisms of longevity, but also provide novel ideas for network-based approaches for longevity-related research.
