They’re not just for supervillains anymore.
Scientists in Japan and Germany have made a breakthrough in the field of solar lasers—and they’ve changed the game completely.
🤯 You like badass science. So do we. Let’s nerd out over it together.

The Horizon 2020 EU-funded MOSAR project (MOdular Spacecraft Assembly and Reconfiguration) aims to develop a ground demonstrator for on-orbit modular and reconfigurable satellites.
The project will investigate and demonstrate technologies that enable a fundamental paradigm shift in satellite design and deployment that could potentially impact all future space missions.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 821966.
Contact: [email protected]
Website: https://www.h2020-mosar.eu/
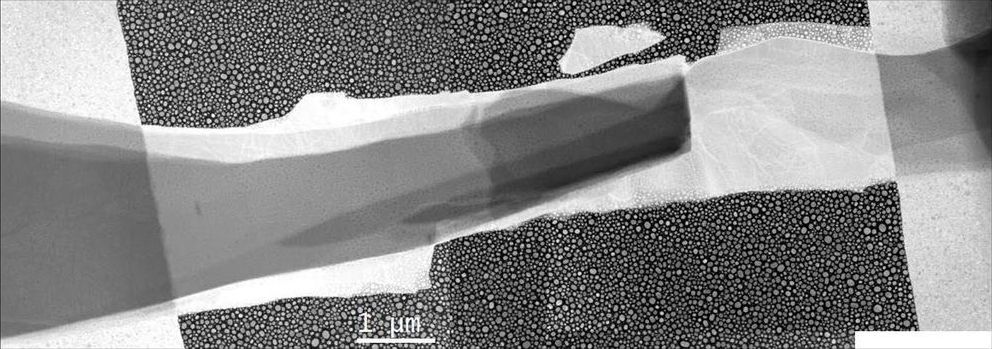
How do you keep the world’s tiniest soda cold? UCLA scientists may have the answer.
A team led by UCLA physics professor Chris Regan has succeeded in creating thermoelectric coolers that are only 100 nanometers thick—roughly one ten-millionth of a meter—and have developed an innovative new technique for measuring their cooling performance.
“We have made the world’s smallest refrigerator,” said Regan, the lead author of a paper on the research published recently in the journal ACS Nano.

From business to leisure to everything in between, technology can make our lives easier and more enjoyable. Further, tech can also be used to promote the common good and make a positive impact on humanity. When an innovation can do both, it’s something truly special and important that deserves our attention.
As industry leaders, the members of Forbes Technology Council stay on top of current trends and developments, including the most exciting and impactful new technology out there. Below, 15 of them share the coolest products and services they’ve seen that are making a real difference in the world.


About 25% of all patents filed by projects supported by Horizon 2020 have come from ERC projects, even though commercialization of research is not the agency’s main aim. Bourguignon and his colleagues rightly argue that many advances in fundamental research ultimately contribute to innovation and benefit society. But that is a hard message to get across at a time of constrained funding and competing priorities.
Europe’s flagship science agency will be crucial to a post-coronavirus world. Slashing its budget will be a senseless act.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is about to carry what will soon become the International Space Station’s first privately-built airlock.
The company has previously built standardized boxes for space-based experiments and tiny satellite deployers, The Verge reports.
The Bishop is shaped like a bell jar and attaches itself to the outside of the space station using a number of clamps and latches.
“Once it’s there, it’s just extra real estate until we want to use it,” Mike Lewis, Nanoracks’ chief innovation officer, told The Verge. “We can use it in a number of ways, the first of which is to bring things outside.”
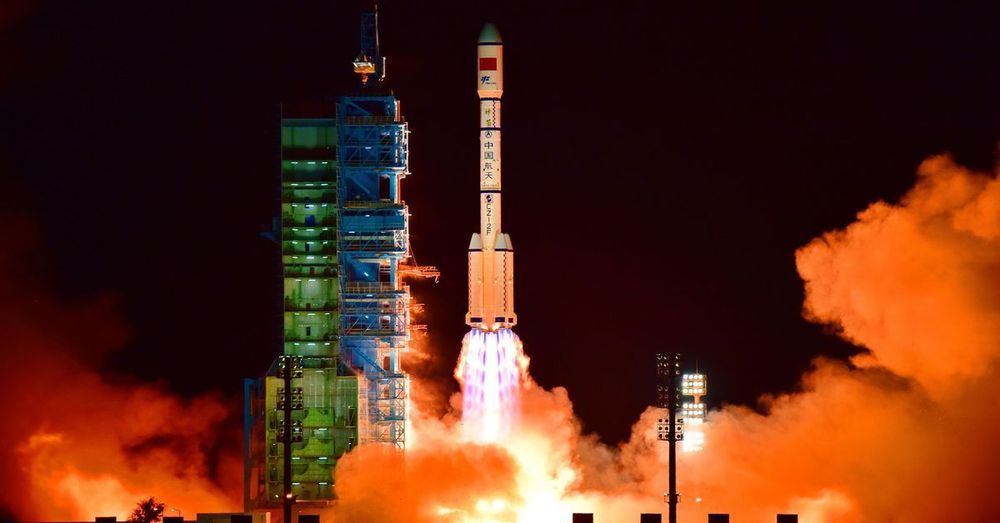

Chinese state media says the country has safely landed a reusable spacecraft which it claims will provide a “convenient and inexpensive” method of getting to and from space. The craft launched on September 4th and landed on September 6th after spending two days in orbit, according to the state-run Xinhua News Agency.


How does #Taiwan connect with the #future through #5G?
https://bit.ly/33b4gmP from Neurozo Innovation
2020 is an epoch-making year of 5G technology for many countries, and Taiwan, too, has shown great enthusiasm for participating in this game. In this article, we will be introducing the 5G strategies and developments in Taiwan.
#technology #telecoms #telecommunications #innovation