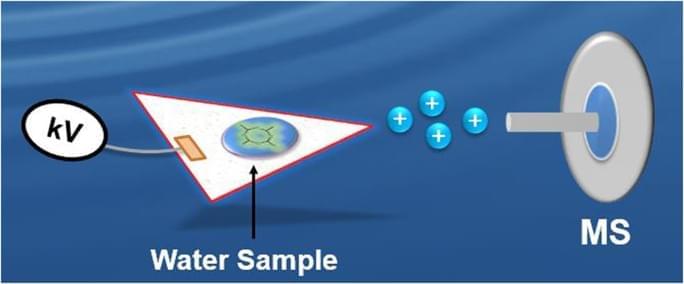
Circa 2016 Basically means we can see contaminated water easier.
Detection and quantification of contaminants or pollutants in surface waters is of great importance to ensure safety of drinking water and for the aquatic environment1,2,3,4,5,6. Metaldehyde (CH3CHO)4 is a cyclic tetramer of acetaldehyde and is used extensively around the world as a molluscicide in agriculture for the control of slugs to protect crops. Large amounts of metaldehyde residues (from ‘slug pellets’) become mobilized, especially during periods of rainfall, seeping into reservoirs, rivers and groundwater, from which drinking water is sourced. Although metaldehyde has low toxicity, cases of metaldehyde poisoning and death in both humans and animals have been reported6,7,8. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) re-registered metaldehyde as a ‘restricted use pesticide’ and required risk-reduction measures to be adopted due to the potential short-term and long-term effects on wildelife9,10. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies metaldehyde as a “moderately hazardous” pesticide (class II)11. In Europe, the European Commission has adopted a directive that restricts pesticides levels to 0.1 μg/L in drinking water12,13. Water companies and environmental agencies are under increasing pressure to routinely monitor levels of metaldehyde residues in water courses as part of their legal obligation14. As such there is an increasing need to develop effective analytical methods for detecting and quantifying metaldehyde in water samples at the source. In particular in-situ monitoring is required to ensure water management practices are based on empirical, up-to-date information which provides a better understanding of competing factors, risk and requirement.
Rapid analytical methods for in-situ analysis of metaldehyde in water, if available, would provide critical information on water quality for water companies and regulation bodies to manage exposures. Quantitative analysis of metaldehyde has been reported using various ex-situ methods based on solid-phase extraction8,15 followed by gas chromatography (GC) or high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with mass spectrometry (MS)7,14,15,16,17,18. However, each of these analytical methods involves extensive sample preparation including extraction, separation, and derivatization, resulting in increased cost and time of analysis. As will be demonstrated in this study, ambient ionization (AI) combined with tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) can overcome such limitations19,20,21,22.
AI is a form of ionization that is performed on unmodified samples in open air and the method is capable of providing almost instantaneous data while minimizing sample preparation22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29. Some of the most popular AI techniques include desorption electrospray ionization (DESI)30, extractive electrospray ionization (EESI)31,32,33,34,35,36, desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI)37,38,39, and direct analysis in real time (DART)40,41. AI-MS shows promise as an analytical tool for in-situ applications and has been demonstrated in a variety of fields where timely intervention is highly desirable such as: homeland security23, food safety42, pharmaceutical drug development43, and environmental monitoring44. There are several advantages to using in-situ AI methods capable of onsite analysis.