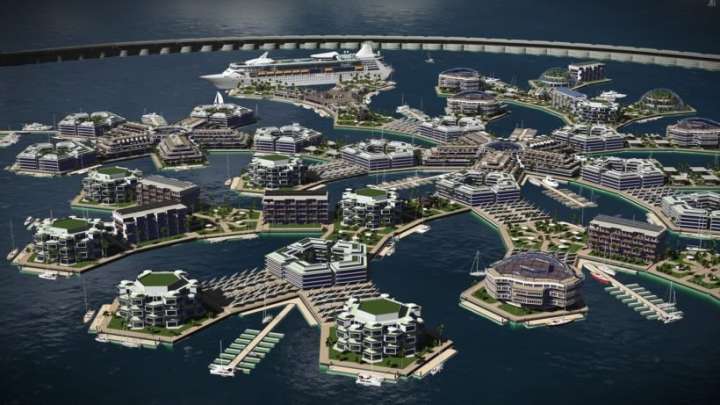
In the hopes of rising above the laws and regulations of terrestrial nations, a group of Silicon Valley millionaires has bold plans to build a floating city in Tahiti, French Polynesia. It sounds like the start of a sci-fi dystopia (in fact, this is the basic premise behind the video game Bioshock), but the brains behind the project say their techno-libertarian community could become a paradise for technological entrepreneurship and scientific innovation.
The Seasteading Institute was set up in 2008 by billionaire PayPal founder Peter Thiel and software engineer, poker player, and political economic theorist Patri Friedman. Both ardent libertarians, their wide-eyed mission is to “establish permanent, autonomous ocean communities to enable experimentation and innovation with diverse social, political, and legal systems.”
“Seasteading will create unique opportunities for aquaculture, vertical farming, and scientific and engineering research into ecology, wave energy, medicine, nanotechnology, computer science, marine structures, biofuels, etc,” their website reads.