What if reversing cellular aging could be achieved by overexpressing just a single gene? In this video, I break down Shift Bioscience’s latest preprint, whic…
Category: life extension – Page 35

A 41-year-old longevity doctor says his ‘biological age’ is 24. He takes 3 supplements daily
Dr. Mohammed Enayat has access to all sorts of experimental antiaging treatments at his clinic, but a core part of his longevity routine is pretty cheap and accessible: supplements.
Enayat told Business Insider that his most recent “biological age” tests, taken 18 months ago, said he was 24, or 17 years younger than his chronological age of 41. There’s no consensus on how to define or measure biological age, but Enayat used GlycanAge and TruAge PACE, which measure inflammation and epigenetics, respectively.
The primary care doctor, who’s also the founder of London’s Hum2n longevity clinic, has been closely tracking his health for the past seven years, using wearable tech, including an Oura ring and a Whoop strap, plus regular blood, urine, and microbiome tests.
Low Uric Acid Is Associated With A Higher Odds Of Living To 100y
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
We Are Building a Future Free of Age-Related Disease
SENS Research Foundation works to develop, promote, and ensure widespread access to therapies that cure and prevent the diseases and disabilities of aging by comprehensively repairing the damage that builds up in our bodies over time.

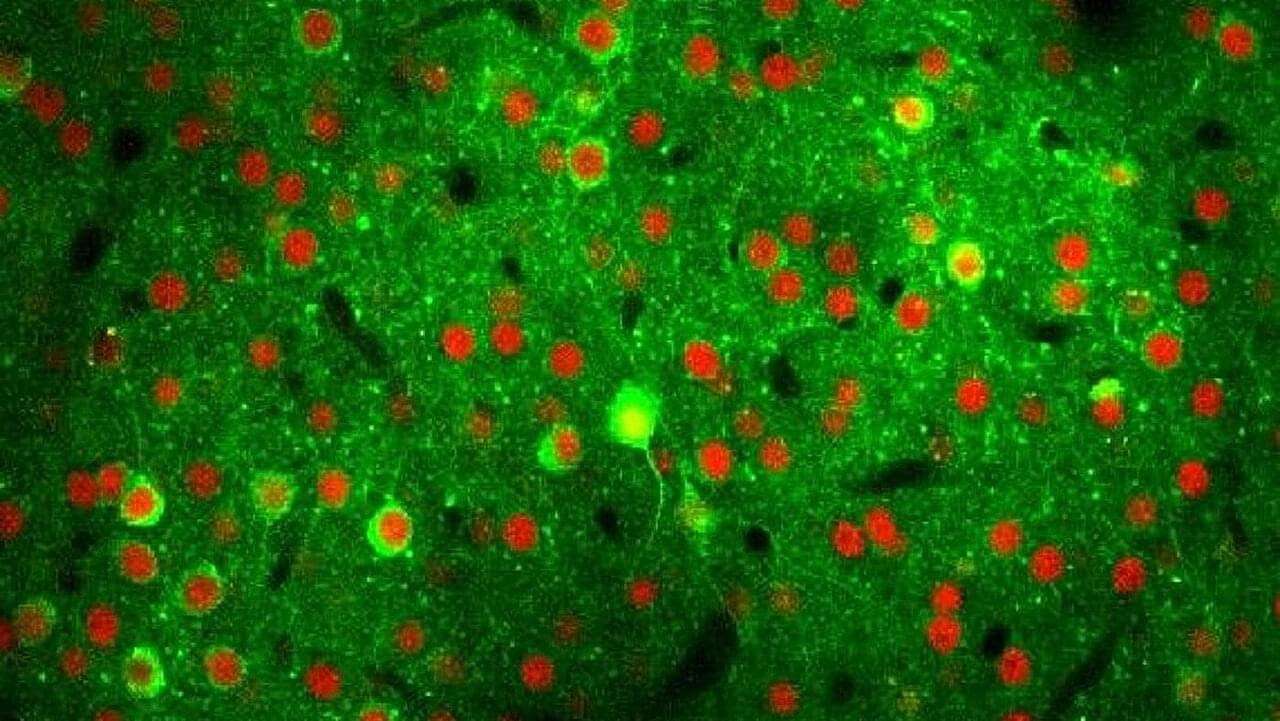
Neighborly help in the brain: Cerebral cortex networks rapidly reorganize to compensate for lost neurons
How the brain largely maintains its function when neurons are lost—this is what researchers at the University Medical Center Mainz, the Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies (FIAS) and Hebrew University (Jerusalem) have deciphered. They show that neuronal networks in the cerebral cortex reorganize within a short period of time, with other nerve cells taking over the tasks of the lost neurons.
These findings could form the basis for future research into natural aging processes and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s. The study is published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Nerve cells (neurons) are the most important building blocks of the brain. They form the basis for all mental and physical functions such as thinking, feeling, movement, and perception. In the course of life, nerve cells in the brain can be lost for various reasons: They die off due to age-related processes, are damaged by toxins such as alcohol, or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s lead to a more rapid progressive loss of neurons.



