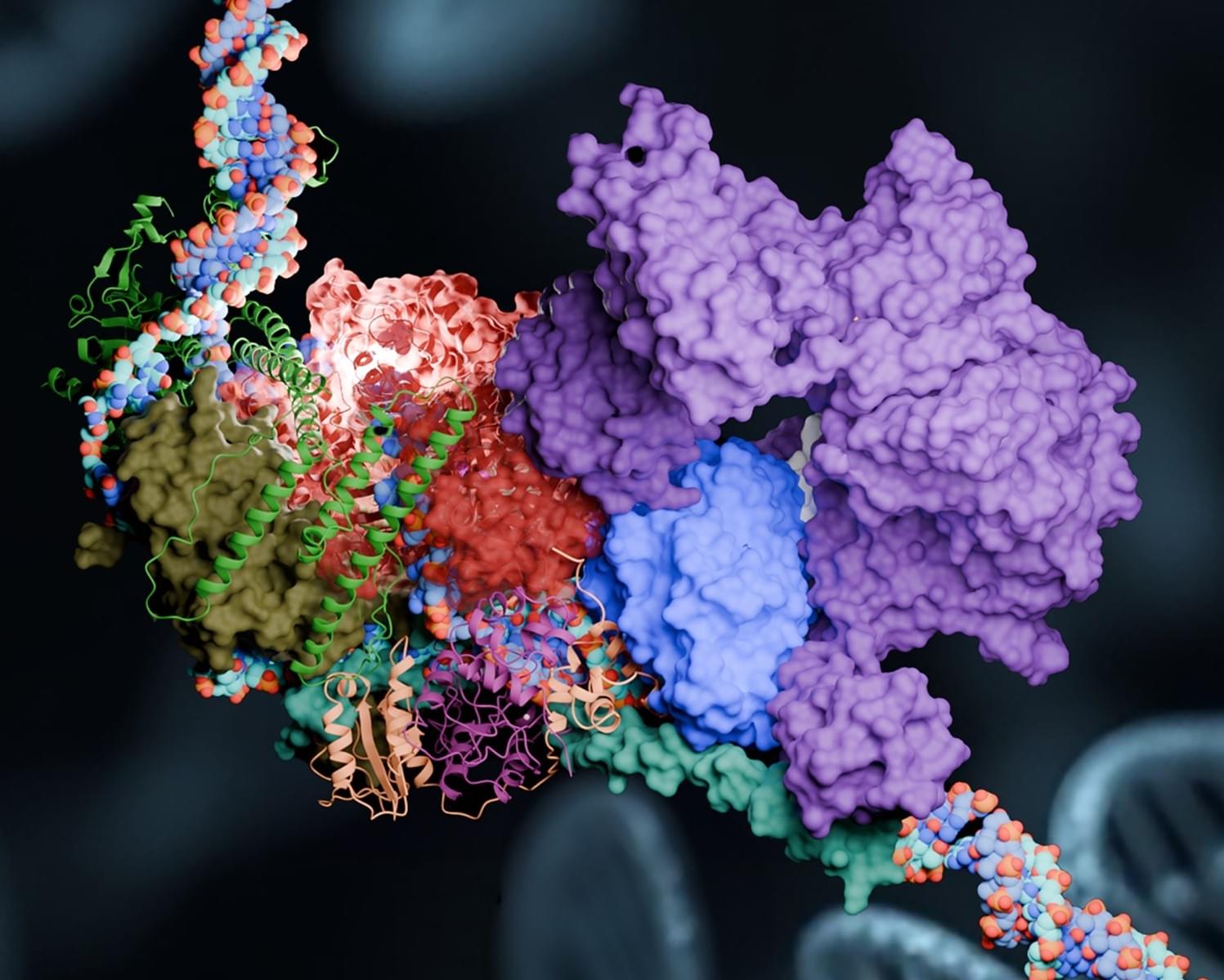
Sunburns and aging skin are obvious effects of exposure to harmful UV rays, tobacco smoke and other carcinogens. But the effects aren’t just skin deep. Inside the body, DNA is literally being torn apart.
Understanding how the body heals and protects itself from DNA damage is vital for treating genetic disorders and life-threatening diseases such as cancer. But despite numerous studies and medical advances, much about the molecular mechanisms of DNA repair remains a mystery.
For the past several years, researchers at Georgia State University tapped into the Summit supercomputer at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to study an elaborate molecular pathway called nucleotide excision repair, or NER relies on an array of highly dynamic protein complexes to cut out, or excise, damaged DNA with surgical precision.