Who wants to live forever? Thanks to these scientific breakthroughs, increased lifespans and reverse aging could be possible.


Aging may seem like the most natural—and inevitable—thing in life. Yet according to a new study in Nature Medicine, rejuvenating an aging body may be as easy as kitchen renovations. Simply swap drill and hammer for a cocktail of two drugs already on the market; rather than pulling out decrepit cabinets, kill off aged “zombie” cells.
These so-called senescent cells are a curious oddity: they’re frail, beat-up, and unable to perform their usual roles. Yet they simply refuse to die. What’s more, zombie cells actively leak inflammatory chemicals into their surroundings, damaging nearby tissue and—in a sense—“spreading” the negative effects of aging.
Yet because they’re extremely rare, amounting to only eight percent of the body’s cells at most, scientists have long wondered just how much they contribute to the aging process.

It was a major feature for the #transhumanism and life extension movements, seen by likely millions of people because it was translated into various languages via international syndication. Story by Richard Godwin. https://www.thetimes.co.uk/article/zoltan-istvan-the-poster-…-lrbx66lqn

Aging may be regulated by a discrete set of intracellular proteins including the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) kinase. mTOR functions within two multiprotein complexes called TORC1 and TORC2. Inhibition of TORC1 has extended life span in every species studied to date and ameliorated multiple aging-related pathologies including declining immune function. Mannick et al. now show that low-dose TORC1 inhibitor therapy in elderly humans decreased the incidence of all infections, improved influenza vaccination responses, and up-regulated antiviral immunity. Thus, targeting the TORC1 pathway that regulates aging may have clinical benefits for elderly humans including improvement in immune function and decreased infection rates.
Inhibition of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) protein kinase extends life span and ameliorates aging-related pathologies including declining immune function in model organisms. The objective of this phase 2a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial was to determine whether low-dose mTOR inhibitor therapy enhanced immune function and decreased infection rates in 264 elderly subjects given the study drugs for 6 weeks. A low-dose combination of a catalytic (BEZ235) plus an allosteric (RAD001) mTOR inhibitor that selectively inhibits target of rapamycin complex 1 (TORC1) downstream of mTOR was safe and was associated with a significant (P = 0.001) decrease in the rate of infections reported by elderly subjects for a year after study drug initiation. In addition, we observed an up-regulation of antiviral gene expression and an improvement in the response to influenza vaccination in this treatment group.
In a study on murine mtDNA, scientists reversed skin wrinkles and hair loss.
In what appears to be a world first, scientists at the University of Alabama at Birmingham have reversed two of the most common visual signs of aging—skin wrinkles and hair loss—in mice by turning off a gene responsible for mitochondrial dysfunction [1].
Study abstract
Australian researchers have made a discovery about telomeres that may have implications for aging, heart disease, cancer, and other age-related diseases.
So, what are telomeres?
Each of the chromosomes that store our genetic information has a telomere at each end. This protective cap consists of a specific DNA sequence that is repeated thousands of times and has two purposes: firstly, it protects the coding regions of the chromosomes and prevents them from being damaged, and secondly, it acts as a clock that controls the number of replications a cell can undergo; this is thought to act as a quality control system to ensure that aged and potentially damaged cells do not remain in circulation.

BIRMINGHAM, Ala. — Wrinkled skin and hair loss are hallmarks of aging. What if they could be reversed?
Keshav Singh, Ph.D., and colleagues have done just that, in a mouse model developed at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. When a mutation leading to mitochondrial dysfunction is induced, the mouse develops wrinkled skin and extensive, visible hair loss in a matter of weeks. When the mitochondrial function is restored by turning off the gene responsible for mitochondrial dysfunction, the mouse returns to smooth skin and thick fur, indistinguishable from a healthy mouse of the same age.
“To our knowledge, this observation is unprecedented,” said Singh, a professor of genetics in the UAB School of Medicine.

http://undoing-aging.org/videos/doug-ethell-presenting-at-undoing-aging-2018
Btw: the facebook event page for Undoing Aging 2019 is already up fb.com/events/2044104465916196/
Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with many mitochondrial diseases, most of which are the result of dysfunctional mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Mitochondrial OXPHOS accounts for the generation of most of the cellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in a cell. The OXPHOS function largely depends on the coordinated expression of the proteins encoded by both nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. The human mitochondrial genome encodes for 13 polypeptides of the OXPHOS, and the nuclear genome encodes the remaining more than 85 polypeptides required for the assembly of OXPHOS system. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) depletion impairs OXPHOS that leads to mtDNA depletion syndromes (MDSs)1, 2. The MDSs are a heterogeneous group of disorders, characterized by low mtDNA levels in specific tissues. In different target organs, mtDNA depletion leads to specific pathological changes. MDS results from the genetic defects in the nuclear-encoded genes that participate in mtDNA replication, and mitochondrial nucleotide metabolism and nucleotide salvage pathway1, 4,5,6,7,8,9,10. mtDNA depletion is also implicated in other human diseases such as mitochondrial diseases, cardiovascular11, 12, diabetes13,14,15, age-associated neurological disorders16,17,18, and cancer19,20,21,22,23,24,25.
A general decline in mitochondrial function has been extensively reported during aging26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33. Furthermore, mitochondrial dysfunction is known to be a driving force underlying age-related human diseases16,17,18, 34,35,36. A mouse that carries elevated mtDNA mutation is also shown to present signs of premature aging37, 38. In addition to mutations in mtDNA, studies also suggest a decrease in mtDNA content and mitochondrial number with age27, 29, 32, 33, 39. Notably, there is an age-related mtDNA depletion in a number of tissues40,41,42. mtDNA depletion is also frequently observed among women with premature ovarian aging43. Low mtDNA copy number is linked to frailty and, for a multiethnic population, is a predictor of all-cause mortality44. A recent study revealed that humans on an average lose about four copies of mtDNA every ten years. This study also identified an association of decrease in mtDNA copy number with age-related physiological parameters39.
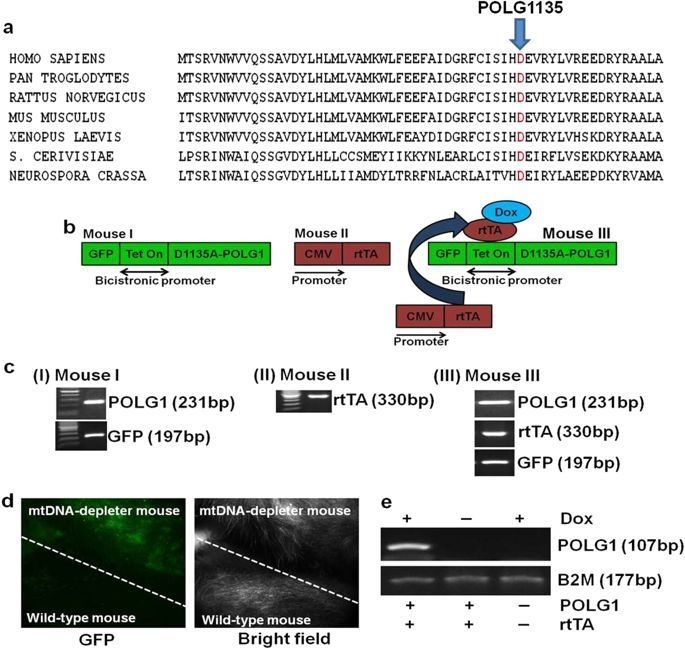
To help define the role of mtDNA depletion in aging and various diseases, we created an inducible mouse expressing, in the polymerase domain of POLG1, a dominant-negative (DN) mutation that induces depletion of mtDNA in the whole animal. Interestingly, skin wrinkles and visual hair loss were among the earliest and most predominant phenotypic changes observed in these mice. In the present study, we demonstrate that mtDNA depletion-induced phenotypic changes can be reversed by restoration of mitochondrial function upon repletion of mtDNA.

Life extension would allow everyone to enjoy a higher degree of freedom.
Freedom is a rather big deal in this age. We want freedom of speech, political freedom, press freedom, religious freedom, and freedom of choice over anything that may concern us directly. Different kinds of freedom are available in different amounts in different areas of the world, and while many people tend to see the glass half empty and complain that freedom is not equally distributed everywhere, it’s undeniable that we enjoy far greater liberty than previous generations. It’s not always easy to act upon your choices, and sometimes you’re free to choose in theory but not in practice, but overall, we enjoy options that who came before us couldn’t even dream of.
Take health, for example. Two hundred years back, if you didn’t want to get the flu, or any other infectious disease, you didn’t have the option not to do so. The mechanism through which infectious diseases manifest and spread wasn’t even remotely understood, so you didn’t have any idea what you should or shouldn’t do to minimize your risk of falling ill; basic hygiene wasn’t exactly a standard, and drugs and vaccines were nowhere in sight. If you actively wanted to do something to prevent getting the flu—which, at the time, might have killed you—you simply didn’t have this option.
Today, however, if you want to avoid infectious diseases, you have plenty of options to do so. Hygiene is common in most of the world, and there are vaccines available. You may well choose to not care, live in filth, and never get even a flu shot, but you do have the option. It’s a choice that, two hundred years back, could simply not be made. Depending on where you live and your access to medical care, acting upon your choice can be difficult, but this is a different matter. The option of preventing disease exists, and in principle, you may avail yourself of it, unlike in the past, when the option wasn’t there to begin with.