Protecting pneumococcal infection in elderly.
The researchers. provide insights into mechanisms underlying respiratory bacterial susceptibility in the elderly.
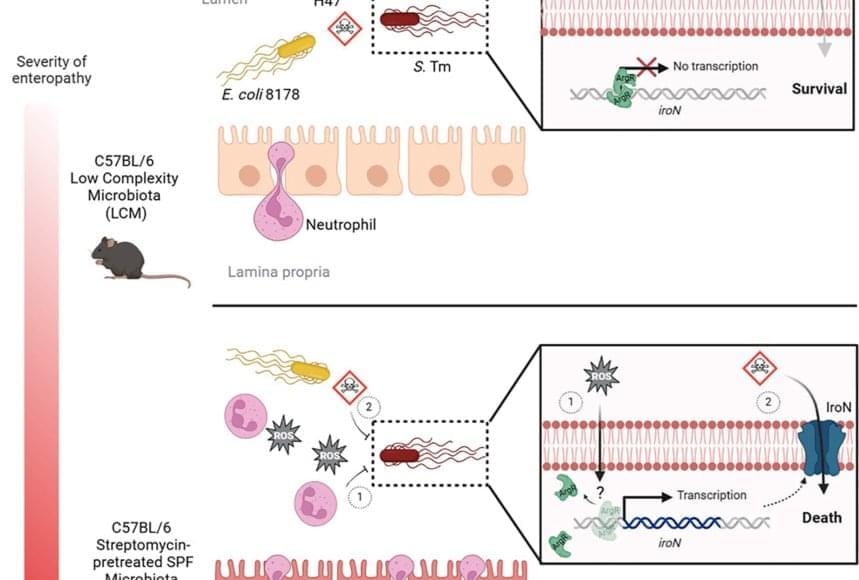
Circadian rhythms is impaired in the aging process. The authors wanted to figure out the relation ship between impaired circadian rhythm and bacterial infections during aging.
They demonstrate that the altered circadian expression of the nuclear receptor Rev-erb-a and the apelin/apelin receptor (APJ) in aged lungs associates with dysregulated time-of-day control of pulmonary immune defenses against pneumococcal infections.
The authors found an interaction between Rev-erb-α and the apelinergic axis that controls host defenses against S. pneumoniae via alveolar macrophages. Pharmacological repression of Rev-erb-α in elderly mice resulted in greater resistance to pneumococcal infection. https://sciencemission.com/pneumococcal-infection-in-elderly
Silva Angulo et al. provide insights into mechanisms underlying respiratory bacterial susceptibility in the elderly. The authors demonstrate that the altered circadian expression of the nuclear receptor Rev-erb-α and the apelin/apelin receptor (APJ) in aged lungs associates with dysregulated time-of-day control of pulmonary immune defenses against pneumococcal infections.