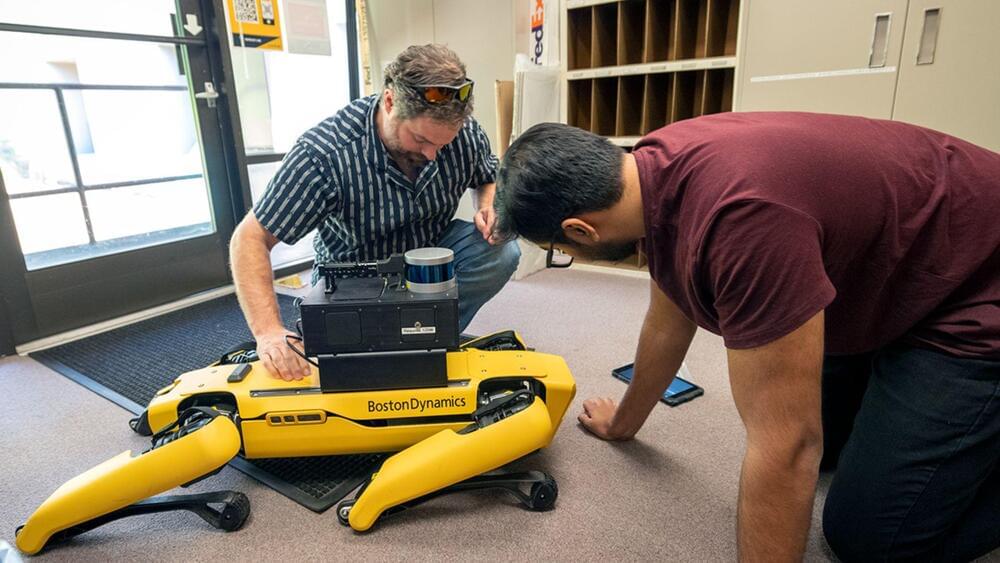
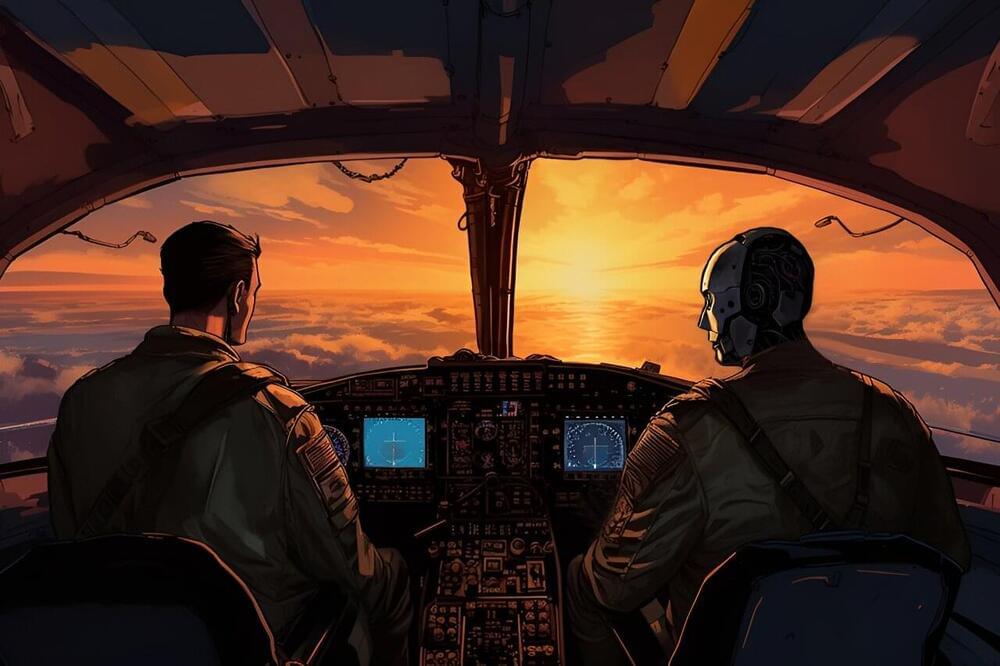
Imagine you’re in an airplane with two pilots, one human and one computer. Both have their “hands” on the controllers, but they’re always looking out for different things. If they’re both paying attention to the same thing, the human gets to steer. But if the human gets distracted or misses something, the computer quickly takes over.
Meet the Air-Guardian, a system developed by researchers at the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). As modern pilots grapple with an onslaught of information from multiple monitors, especially during critical moments, Air-Guardian acts as a proactive co-pilot; a partnership between human and machine, rooted in understanding attention.
But how does it determine attention, exactly? For humans, it uses eye-tracking, and for the neural system, it relies on something called “saliency maps,” which pinpoint where attention is directed. The maps serve as visual guides highlighting key regions within an image, aiding in grasping and deciphering the behavior of intricate algorithms. Air-Guardian identifies early signs of potential risks through these attention markers, instead of only intervening during safety breaches like traditional autopilot systems.