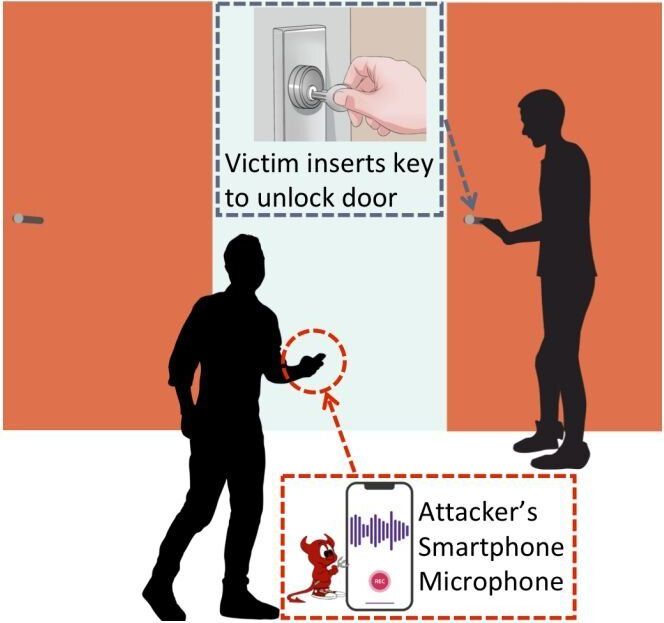
A trio of researchers has found a way to pick an ordinary physical lock using a smartphone with special software. The three, Soundarya Ramesh, Harini Ramprasad, and Jun Han, gave a talk at a workshop called HotMobile 2020 at this year’s International Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, outlining their work.
With traditional locks, such as those found on the front doors of most homes, a person inserts the proper (metal) key and then turns it. Doing so pushes up a series of pins in the lock by a certain amount based on the ridges on the key. When the pins are pushed in a way that matches a preset condition, the tumbler can turn, retracting the metal piece of the door assembly from its berth, allowing the door to open. In this new effort, the researchers have found that it is possible to record the sounds made as the key comes into contact with the pins and then as the pins move upward, and use software to recreate the conditions that produce the same noises. Those conditions can be used to fabricate a metal key to unlock the door. The result is a system the team calls SpiKey, which involves use of a smartphone to record lock clicks, decipher them and then create a key signature for use in creating a new metal key.
The researchers acknowledged in their presentation that the weak link in their system is recording the key unlocking the door. Because of its nature, they assume that the recording would have to be done secretly so as to not alert a homeowner that their lock is being picked. They suggest that several possible options for wrongdoers, including walking past while holding a microphone, hiding a microphone nearby, or installing software on the victim’s phone. Each has its own risks, they note, which would minimize the likelihood of run-of-the-mill burglars using such an approach. But for high-profile victims, the effort might be worth the risk. They say that they next plan to investigate ways to foil such attacks by modifying traditional locks.