Circa 2012
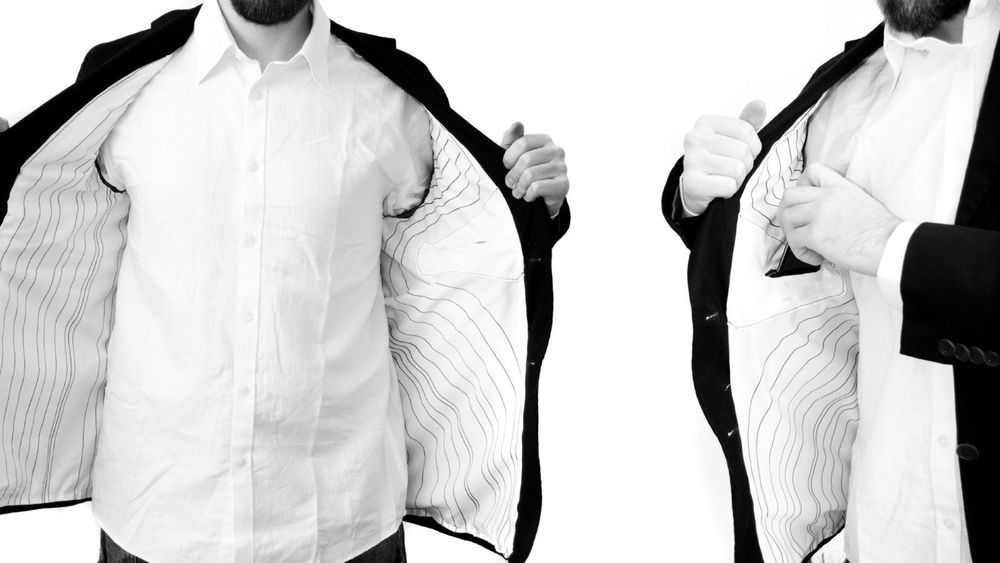
Switching your phone off for important meetings or trips to the cinema can be a pain in the ass. Victor Johansson has a solution, though: he’s designed the Escape Jacket, which features a Faraday cage in the inside pocket to immediately take your phone off the grid.
UK-based designer Johansson says that the concept is all about you-time. He explains:
During the research phase of this project the idea of “time as a luxury” came to be a main theme. After trying to find ways to give people more time I finally ended up with the idea of removing (connected) time instead since luxury is often more about the things you remove than the things you add. The idea is that as soon as you leave work, or just want a break you put your phone in the inner pocket of the jacket and you terminate all connectivity.