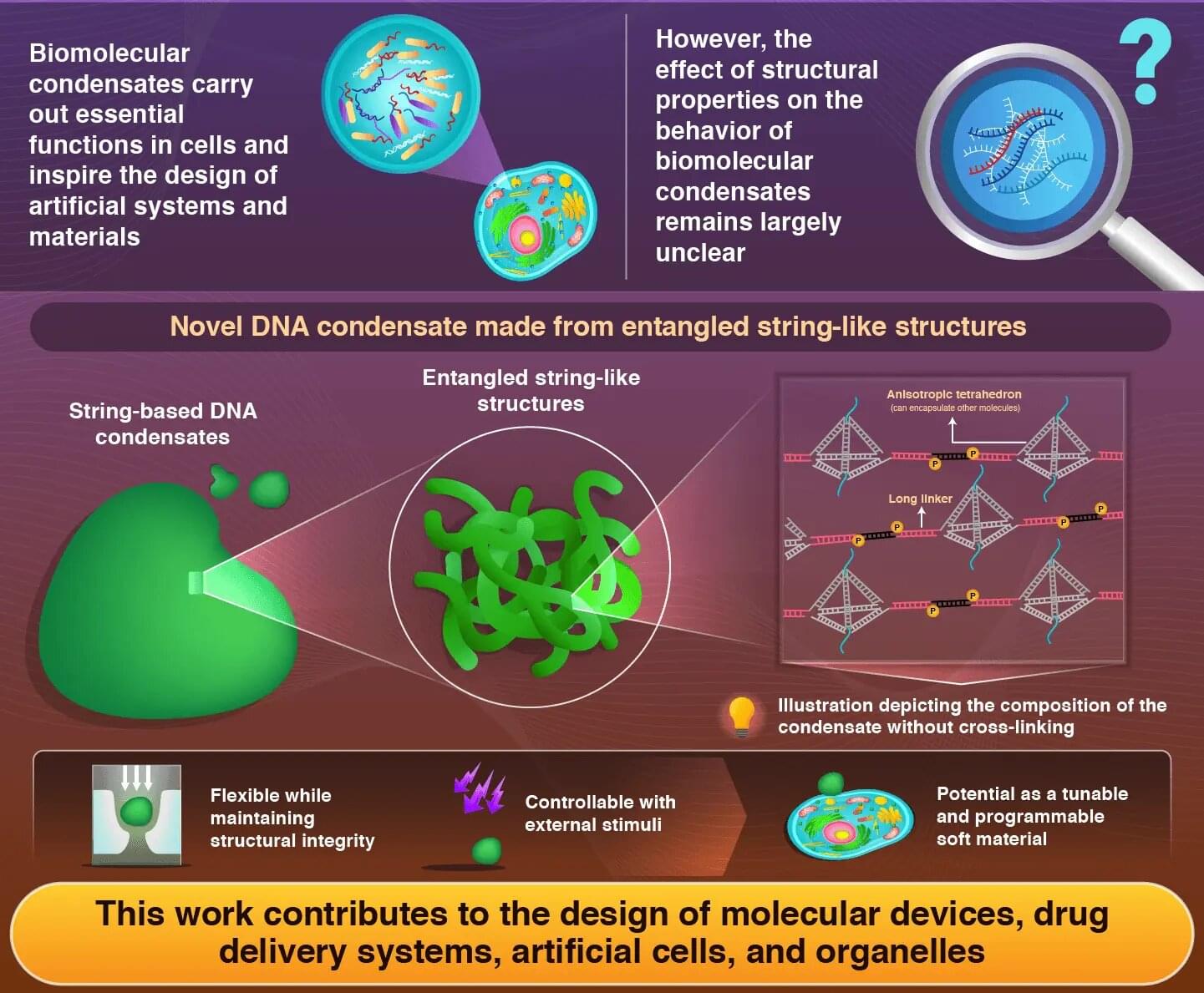
Newly developed DNA nanostructures can form flexible, fluid, and stimuli-responsive condensates without relying on chemical cross-linking, report researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo and Chuo University, in the journal JACS Au.
Owing to a rigid tetrahedral motif that binds the linkers in a specific direction, the resulting string-like structures form condensates with exceptional fluidity and stability. These findings pave the way for adaptive soft materials with potential applications in drug delivery, artificial organelles, and bioengineering platforms.
Within living cells, certain biomolecules can organize themselves into specialized compartments called biomolecular condensates. These droplet-like structures play crucial roles in cellular functions, such as regulating gene expression and biochemical reactions; they essentially represent nature’s clever way of organizing cellular activity without the need for rigid membranes.