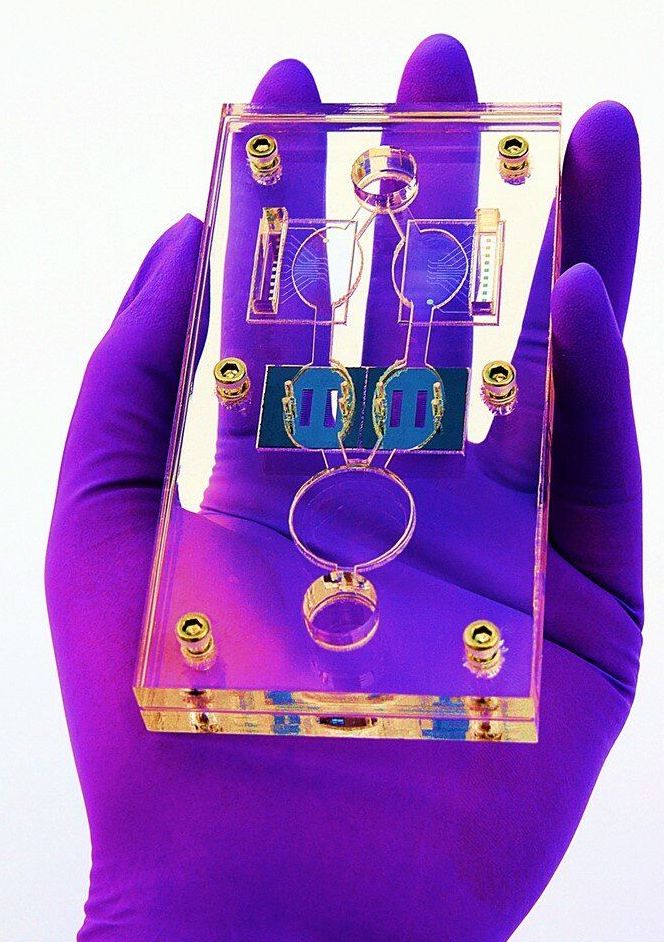
The replacement of animals as test subjects is one step closer to reality with the successful testing of multi-organ “human-on-a-chip” models to recapitulate the 28-day experiments typically used in animals to evaluate the systemic toxicity of drug and cosmetic compounds. As published and featured as a frontispiece in the prestigious peer-reviewed scientific journal Advanced Functional Materials, the microfluidic device with interlinking modules containing human-derived heart, liver, skeletal muscle and nervous system cells was able to maintain cellular viability and record cellular function in real-time for 28 days.
The University of Central Florida (UCF) in collaboration with the Florida biotech firm Hesperos, Inc., has shown that one of its innovative four-organ in vitro (out of body) model systems is able to realistically replicate in vivo (in body) responses to sustained drug dosing of human cells.
“The technology could allow us, in the very near future, to move chronic drug experiments from animal models to these novel human in vitro models,” said Hesperos Chief Scientist James J. Hickman, who is a Professor at UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center.